Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
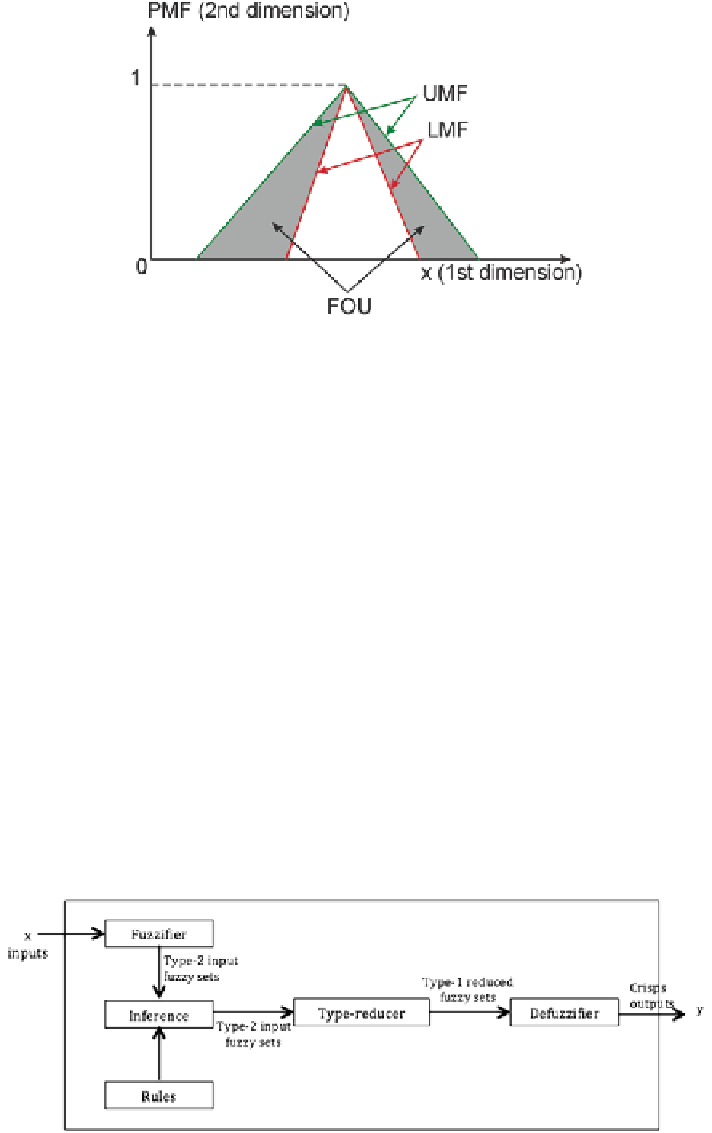
Fig. 2.5
The membership function of an interval type-2 fuzzy set
the consequents, while in the example “if the temperature indicates cold, then
the heater must be switched on”, the fuzzy set 'cold' appears in the antecedents.
Membership functions are used to describe these fuzzy sets.
Experts construct the rules of a FLS considering their experience or data that
have been extracted from experiments or surveys. Therefore, the knowledge and
data that are used to construct the rules of a FLS are uncertain. This uncertainty
leads to rules that have uncertain antecedents and/or consequents, which in turn
translates into uncertain corresponding membership functions (Karnik et al. 1999).
This uncertainty can be handled using type-2 fuzzy sets.
A type-2 FLS is depicted in Fig.
2.6
. Two steps are required to go from an
interval type-2 fuzzy set to a number:
•
Type-reduction
: in this step an interval type-2 fuzzy set is reduced to an interval-
valued type-1 fuzzy set. This is achieved using particular algorithms. There are a
comparable number of type-reduction methods (Mendel 2001).
•
Defuzziication
: In this step the centroid of the type-reduced set is computed.
In particular, the average of the two end-points of the finite interval of numbers,
which has been come off the process of type-reduction, is calculated. In other
words, defuzzification maps the type-1 FS that came of the type-reduction step.
Fig. 2.6
A type-2 rule-based fuzzy logic system
Search WWH ::

Custom Search