Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
of achievement emotions. The use of cognitive theories in student modeling adds
more “human” reasoning to the computer.
1.2.6 Modeling the Uncertainty of Learning
The processes of learning and student's diagnosis are complex. They are defined by
many factors and are depended on tasks and facts that are uncertain and, usually,
unmeasured. The determination of the student's knowledge, mental state and behavior
is not a straightforward task, but it is based on uncertain observations, measurements,
assumptions and inferences. The presence of uncertainty in student's diagnosis is
increased in an adaptive/personalized tutoring system due to either the indirect inter-
action between the learner and the teacher, or the technical difficulties (Grigoriadou
et al. 2002). The most common used techniques to encounter this kind of uncertainty
are fuzzy logic and Bayesian Networks.
1.2.6.1 Fuzzy Student Modeling
Fuzzy logic was introduced by Zadeh (1965) as a methodology for computing with
words. It is able to handle the uncertainty of learning and student's diagnosis, which
is based on imprecise data and human decisions, since it encounters the uncer-
tainty problems that are caused by incomplete data and human subjectivity (Drigas
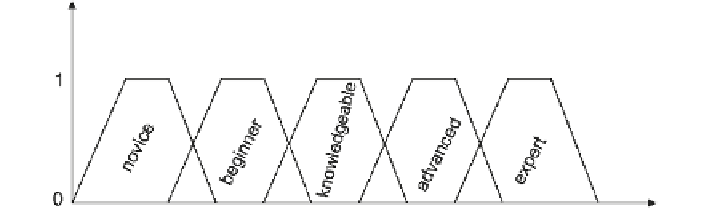
et al. 2009). The core of the fuzzy logic theory is the fuzzy sets, which are used to
describe an element (characteristic, thing, fact or state) and have no concrete limits
(Fig.
1.7
). An element can belong to two adjacent fuzzy sets at the same time, but
with different membership degree. For example, a student can be 85 % advanced
(membership degree: 0.85) and 15 % expert (membership degree: 0.15) or 30 %
novice (membership degree: 0.3) and 70 % beginner (membership degree: 0.7)
(Fig.
1.8
).
Fuzzy logic can help to improve the adaptation of an intelligent tutoring system.
Fuzzy logic can help the system to decide what is the appropriate instruction model
Fig. 1.7
Fuzzy sets of the students knowledge level
Search WWH ::

Custom Search