Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
The perturbation model has a collection of mistakes, which is usually called
bug library. The bug library and can be built either by empirical analysis of mis-
takes (enumerative technique) or by generating mistakes from a set of common
misconceptions (generative technique). In enumerative technique, the designers
and analysts of the system determine the possible errors that a student can make
(Smith 1998). In generative modeling the system uses a cognitive model, which
considers students' behavior, to detect students' errors (Clancey 1988).
1.2.3.2 Constraint-Based Model
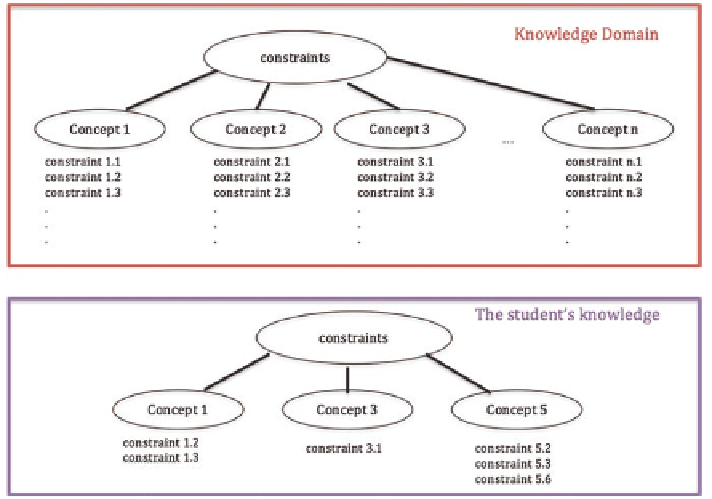
The Constraint-Based Model (CBM) uses constraints to represent both domain and
student knowledge. The knowledge domain is represented as set of constraints and
the student model is the set of constraints that have been violated (Fig.
1.6
). A con-
straint has a satisfaction clause and a relevance condition. If the satisfaction clause
becomes false for the relevance condition, then the learner has made an error (Martin
1999). The particular model is based on Ohlsson's theory of learning from errors
(Ohlsson 1996). According to this theory a learner often makes mistakes when per-
forming a task, even when s/he has been taught the correct way to do it. According to
Mitrovic et al. (2001), the most important advantages of CBM are: its computational
simplicity, the fact that it does not require a runnable expert module, and the fact that
it does not require extensive studies of student bugs as in enumerative modeling.
Fig. 1.6
Constraint-based model
Search WWH ::

Custom Search