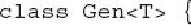Java Reference
In-Depth Information
The output produced by the program is shown here:
Let's examine this program carefully. First, notice how
Gen
is declared by the following
line:
Here,
T
is the name of a
type parameter
. This name is used as a placeholder for the actual
type that will be passed to
Gen
when an object is created. Thus,
T
is used within
Gen
whenever the type parameter is needed. Notice that
T
is contained within
< >
. This syn-
tax can be generalized. Whenever a type parameter is being declared, it is specified within
angle brackets. Because
Gen
uses a type parameter,
Gen
is a generic class.
In the declaration of
Gen
, there is no special significance to the name
T
. Any valid iden-
tifier could have been used, but
T
is traditional. Furthermore, it is recommended that type
parameter names be single-character, capital letters. Other commonly used type parameter
names are
V
and
E
.
Next,
T
is used to declare an object called
ob
, as shown here:
As explained,
T
is a placeholder for the actual type that will be specified when a
Gen
object
is created. Thus,
ob
will be an object of the type passed to
T
. For example, if type
String
is passed to
T
, then in that instance,
ob
will be of type
String
.
Now consider
Gen
's constructor: