Java Reference
In-Depth Information
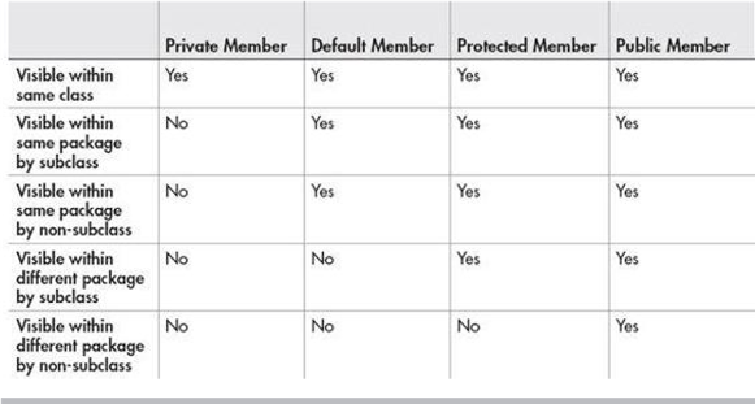
Table 8-1
Class Member Access
If a member of a class has no explicit access modifier, then it is visible within its package
but not outside its package. Therefore, you will use the default access specification for ele-
ments that you want to keep private to a package but public within that package.
Members explicitly declared
public
are visible everywhere, including different classes
and different packages. There is no restriction on their use or access. A
private
member is
accessible only to the other members of its class. A
private
member is unaffected by its
membership in a package. A member specified as
protected
is accessible within its pack-
age and to all subclasses, including subclasses in other packages.
Table 8-1
applies only to members of classes. A top-level class has only two possible
access levels: default and public. When a class is declared as
public
, it is accessible by any
other code. If a class has default access, it can be accessed only by other code within its
same package. Also, a class that is declared
public
must reside in a file by the same name.
A Package Access Example
In the
package
example shown earlier, both
Book
and
BookDemo
were in the same pack-
age, so there was no problem with
BookDemo
using
Book
because the default access priv-
ilege grants all members of the same package access. However, if
Book
were in one pack-
age and
BookDemo
were in another, the situation would be different. In this case, access
to
Book
would be denied. To make
Book
available to other packages, you must make