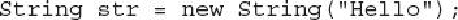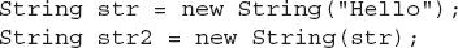Java Reference
In-Depth Information
the string "In Java, strings are objects." is automatically made into a
String
object by Java.
Thus, the use of the
String
class has been “below the surface” in the preceding programs.
In the following sections, you will learn to handle it explicitly. Be aware, however, that the
String
class is quite large, and we will only scratch its surface here. It is a class that you
will want to explore on its own.
Constructing Strings
You can construct a
String
just like you construct any other type of object: by using
new
and calling the
String
constructor. For example:
This creates a
String
object called
str
that contains the character string "Hello". You can
also construct a
String
from another
String
. For example:
After this sequence executes,
str2
will also contain the character string "Hello".
Another easy way to create a
String
is shown here:
In this case,
str
is initialized to the character sequence "Java strings are powerful."
Once you have created a
String
object, you can use it anywhere that a quoted string is
allowed. For example, you can use a
String
object as an argument to
println( )
, as shown
in this example: