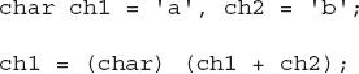Java Reference
In-Depth Information
Somewhat counterintuitively, no cast is needed when assigning
b*b
to
i
, because
b
is
promoted to
int
when the expression is evaluated. However, when you try to assign
b * b
to
b
, you do need a cast—back to
byte
! Keep this in mind if you get unexpected type-in-
compatibility error messages on expressions that would otherwise seem perfectly OK.
This same sort of situation also occurs when performing operations on
char
s. For ex-
ample, in the following fragment, the cast back to
char
is needed because of the promotion
of
ch1
and
ch2
to
int
within the expression:
Without the cast, the result of adding
ch1
to
ch2
would be
int
, which can't be assigned to a
char
.
Casts are not only useful when converting between types in an assignment. For example,
consider the following program. It uses a cast to
double
to obtain a fractional component
from an otherwise integer division.