Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 10.8.
The helicoidal representation of the cut-concave shape. (a) Open curve;
(b) closed curve (from [7]).
Fig. 10.9.
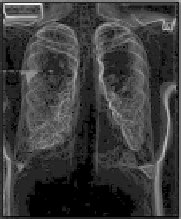
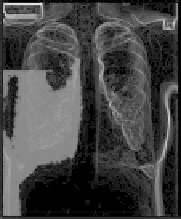
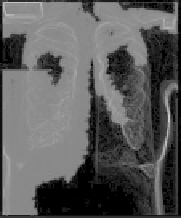
Application of GOGAC to lung Xray image segmentation. Evolution of
the fast marching wavefront from the cut line. (Images provided by Ben Appleton.)
p
cut
along the cut line as the source and the periodic replica of these points
in the cutplane
S
as the destination and then proceed with the binary search
in the same manner as the CSP algorithm. Figure 10.9 shows the evolution
of the fast marching wavefront emanating from the cut line as it segments a
lung using GOGAC. Figures 10.10 and 10.11 show other segmentation results
from the GOGAC method.
10.3.1 Fast Marching Algorithm
We use the Fast Marching algorithm [149] to find the surfaces of minimal
action whose gradient curves form shortest paths, also known as geodesics.
A geodesic is a generalization of the concept of a “straight line” to “curved
spaces” (i.e., Riemannian spaces) such as the surface of the earth. In the case
of a sphere such as the Earth, a geodesic is a great circle. With respect to
a given metric, geodesics are defined to be the shortest path between points
on the space. A shortest path between two points in a curved space can be
Search WWH ::

Custom Search