Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
c
302
302
miRNAs
miRNAs
142 221 4659 30
142 221 4659 30
321 19 206
321 19 206
320
320
29a
29a
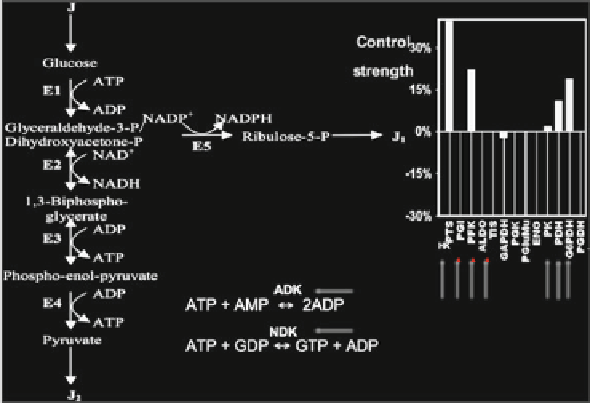
Fig. 4.12 (a) Glycolysis main steps with indication (b) of their enzyme control strengths and of
their inhibitory microRNAs (
red arrows
). E1 denotes the four enzymes of the high glycolysis
(hexokinase HK, phosphoglucose-isomerase PGI, phosphofructo-kinase PFK, and aldolase ALDO),
E2 denotes the glyceraldehyde-3P-dehydrogenase, E3 denotes the three enzymes of the low
glycolysis (phosphoglycerate-kinase, phosphoglycerate-mutase, enolase ENO), E4 denotes the
pyruvate-kinase PK and E5 the three enzymes of the oxidative part of the pentose pathway
(glucose-6P-dehydrogenase G6PDH, 6P-glucono-lactonase, and phosphogluconate-dehydrogenase
PGDH, alternative to phospho-transferase system PTS). (c) Adenylate (guanylate) pool regulated
by ADK (NDK)
inhibited and sufficiently present in the mitochondrial inner membrane [cf. Fig.
4.13
and Demongeot et al. (
2007c
)], or conversely privilege lactacte shuttle [like in brain
astrocytes, in order to feed neurons in lactate (Aubert et al.
2005
;
2007
)].
Glycolysis (Fig.
4.12
) has been modeled by several authors (Aubert et al.
2005
,
2007
; Boiteux et al.
1975
; Demongeot and Seydoux
1979
; Hervagault et al.
1983
;
Demongeot and Kellershohn
1983
; Demongeot and Doncescu
2009b
), especially its
central allosteric step ruled by the phosphofructokinase (PFK), which is the key
glycolytic enzyme, because of its highly nonlinear allosteric kinetics and of the
presence as effectors of ATP and ADP (controlled by miR-298 and 29a in
adenylates/guanylates pools regulated by ADK and DNPK, cf. Table
4.7
)ina
negative regulatory circuit causing, for critical values of the glucose entry flux J,
oscillations for all glycolytic metabolites, with a period of several minutes (Aubert
et al.
2005
; Demongeot and Seydoux
1979
). Let us define now by
x
1
,
x
2
,
x
3,
and
x
4
the concentrations of the successive main metabolites of the glycolysis, respec-
tively glucose, glyceraldehyde-3-P, 1,3-biphospho-glycerate, and phospho-enol-
pyruvate. We assume that steps E2 and E3 of the glycolysis (Fig.
4.12a
) are
Michaelian and reversible. The complex E1 includes the allosteric irreversible
kinetics of the phospho-fructo-kinase PFK with a cooperativity
n
[see Ovadi
(
1988
), Reder (
1988
), Ritter et al. (
2008
), Thellier et al. (
2006
), and Demongeot










Search WWH ::

Custom Search