Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.3
Sequences alignment and distances to AL for
miR136, miR34a, and miR301 (from
their inhibited targets, ATPase and Translocase
helicase function can be controlled by several microRNAs like mi-R20 and
miR-181b and (2) several functions like helicase and endonuclease (resp.
exoribonuclease and polymerase) are controlled by the same microRNA miR-20
(resp. miR-93).
4.4.3 MicroRNas and Cellular Energetics: Oxidative
Phosphorylation
The cellular energy system of most of eukaryotic cells is essentially composed of
glycolysis and aerobic oxidation
.
In eukaryotes, later stages of oxidative phosphor-
ylation occur in mitochondria, with enzymatic steps like ATPase and translocase.
For each of these genes, it is possible to find at least one microRNA inhibiting its
activity (cf. Table
4.3
). The microRNAs exert a translational repression preventing
the enzyme synthesis in ribosomes. For example, in (Bandiera et al.
2011
) are
presented 2 microRNAs susceptible to hybridize with a perfect anti-match
mitochondrial genes: hsa-miR-1974 and hsa-miR-1977 (Fig.
4.11
) target indeed
two mitochondrial tRNA genes, respectively, TRNE and TRNN, which code,
respectively, for ATP8 and ND4L, and the hsa-miR-1978 targets a stretch of a
mitochondrial rRNA sequence called RNR1. ATP8 is the ATP synthase protein 8, a
subunit of the mitochondrial ATPase, and ND4L is a protein which provides
instructions for making NADH. RNR1 is a subunit of the ribonucleotide reductase,

































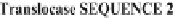






























Search WWH ::

Custom Search