Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
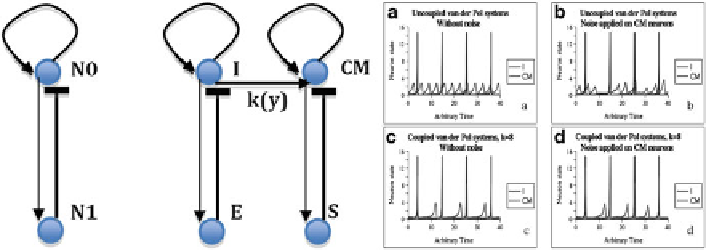
Fig. 4.4
Left
: Structure of a single negative regulon with two nodes, N0 self-excitable and N1, and
2 regulons coupled between their respective self-excitable nodes I and CM by a directional edge
with a coupling intensity
k
(
y
).
Right
: Temporal series from simulations of the 2 negative regulons
(neuron I in
black
and CM in
gray
), in four cases: (a) regulons are uncoupled without noise;
(b) uncoupled with addition of noise to CM neurons; (c) coupled without noise; (d) coupled with
noise. Parameters of the van der Pol equations are
μ ¼
10,
η ¼
1, with
k
(
y
)
¼
0 when systems are
uncoupled and
k
(
y
)
¼
8 when coupled
CM. Both respiratory and cardiac systems have indeed their own rhythm, but they
are also coupled directionally: the cardiomodulator CM is coupled to the respiratory
activity (inspiratory neurons I) via bulbar connections, causing a 1/1 harmonic
entrainment in the case of coupling, perturbed in the case of uncoupling and robust
in the case of coupling, by adding a Gaussian white noise to the second member of
the van der Pol equations [cf. Fig.
4.4
Right and Elena et al. (
2008
) and Demongeot
et al. (
2002
)].
4.3.6 Example of an Asymptotically Stable and Structurally
Instable Genetic Network Controlling Flower
Morphogenesis
The classical network controlling the flowering of
Arabidopsis thaliana
(Demongeot et al.
2010a
; Mendoza and Alvarez-Buylla
1998
) contains two
strongly connected components and has five asymptotically stable attractors. The
relative sizes of the five attraction basins corresponding to these attractors highly
depend on the state of critical nodes as the gibberellin gene called RGA in Fig.
4.5
(plant hormone responsible of the flower growth).
4.3.7 Example of a Non-Robust (Due to a Sensitivity to the
Initial Conditions) Hamiltonian Population Dynamics
Network
V. Volterra introduced his famous differential system for interpreting the
fluctuations observed in the struggle for life between a prey population of size
x
and a predator population of size
y
(Glade et al.
2007
; Volterra
1926a
,
b
,
1931
) and
Search WWH ::

Custom Search