Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
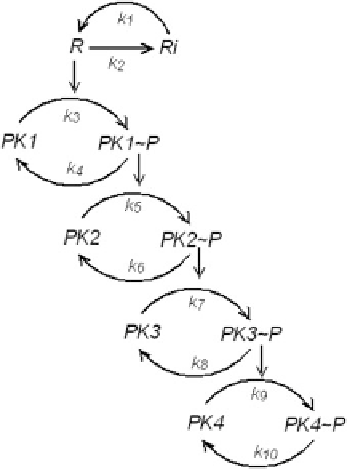
Fig. 3.4 Four steps signal
transduction cascade of
kinases and phosphatases
continued to apply to the maximum level, but now the kinases collectively were
equally important as the phosphatases collectively, not individually. For all other
points in the transient yet another law was derived mathematically, defining control
by time itself (Westerhoff
2008
).
This work had been preceded by an analysis of the cascades in terms of mass
action kinetics by (Heinrich et al.
2002
). In this description, the reaction rate for the
phosphorylation of the next kinase in the pathway reads as follows:
v
iþ
1
¼
k
iþ
1
:
x
i
:
e
i
:ð
1
x
iþ
1
Þ:
e
iþ
1
¼ α
iþ
1
:
x
i
:
e
i
:ð
1
x
iþ
1
Þ;
(3.14)
where
e
i
represents the total concentration of the
i
th kinase in the pathway and
x
i
the fraction of the kinase that is in the phosphorylated, hence active, state.
α
i
+1
is
the pseudo-first-order rate constant. The corresponding phosphatase, at concen-
tration
f
i
+1
,wouldactatarateasfollows:
v
ðiþ
1
Þ
¼
k
ðiþ
1
Þ
:
x
iþ
1
:
e
iþ
1
:
f
iþ
1
¼ β
iþ
1
:
x
iþ
1
:
e
iþ
1
:
(3.15)
's were proportional to the kinase and phosphatase activities
(and concentrations) at the corresponding levels. For the steady state of permanent
activation of the pathway, one then finds
The
α
's and the
β
k
iþ
1
:
x
i
:
e
i
α
iþ
1
:
x
i
:
e
i
x
iþ
1
¼
f
iþ
1
¼
e
iþ
1
:
(3.16)
k
iþ
1
:
x
i
:
e
i
þ
k
ðiþ
1
Þ
:
α
iþ
1
:
x
i
:
e
i
þ β
iþ
1
:

Search WWH ::

Custom Search