Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
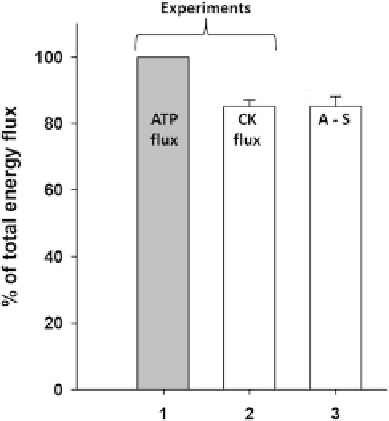
Fig. 11.6 Comparison of experimental data of energy flux measurements with results of
simulations by mathematical models. ATP flux: the rate of ATP synthesis in mitochondria; CK
flux: energy flux carried into cytoplasm by phosphocreatine measured experimentally by the
18
O
transfer method [data summarized from Dzeja and Terzic (
2003
), Dzeja et al. (
1996
,
2001
,
2007
,
2011a
), Pucar et al. (
2001
)]; A-S: Aliev and Saks models of compartmentalized energy transfer
(Dos Santos et al.
2000
; Aliev and Saks
1997
). The mathematical model of the compartmentalized
energy transfer system in cardiac myocytes includes mitochondrial synthesis of ATP by ATP
synthase, PCr production in the coupled MtCK reaction, the myofibrillar and cytoplasmic CK
reactions, ATP utilization by actomyosin ATPase during the contraction cycle, and diffusional
exchange of metabolites between different compartments. The model gives a good fitting with the
experimental data, showing that about 85 % of energy produced in mitochondria as ATP flux is
transferred out of mitochondria as PCr flux, in agreement with the abundant experimental data
reported by Dzeja and colleagues
Recently this method has been used in quantitative studies of metabolic cycles in
human health and disease (Dzeja et al.
2011a
).
11.4.3
Intracellular Energetic Units and Mitochondrial
Interactosome: Local Signaling and Frank-Starling
Law
In addition to the fundamental structural data from Wallimann and Schlattner and
energy flux determinations by Dzeja and Terzic, another important question
concerns the cellular mechanisms involved in the function of CKs and other
phosphotransfer pathways. This question was addressed by the group of Valdur
Saks utilizing permeabilized cells that enable the study of mitochondrial function in
their natural environment (Saks et al.
1991
,
1998
,
2007a
,
d
; Saks and Strumia
Search WWH ::

Custom Search