Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.17 The conserved binding site (in blue) of AL with pb1gene compared across a selection
of influenza viral strains (collected from NCBI new release 715 [22/01/2010])
Fig.
4.17
, an example shows that microRNA hsa-miR-143 presents numerous
perfect matches with Hamming distance 0 between long subsequences (whose
length is between 7 and 11 bases) it shares with genomes of Dengue and Japanese
encephalitis viruses (Demongeot et al.
2009b
,
c
).
In Table
4.16
, several microRNAs (miR-491 and 654) are inhibiting viral H1N1
influenza A proteins like pb1, which is a critical RNA polymerase subunit of the
virus H1N1 influenza A, necessary for the virus replication both in vitro and in vivo
(He et al.
2009
; Song et al.
2010
; Li et al.
2011
).
The microRNAs like miR-491 can also hybridize many strains of several
influenza viruses in conserved viral strains (Table
4.17
), proving the possibility of
an unspecific immunologic defense, acting before the immune cell response and
preventing a too rapid early viral replication in human host. It could be interesting
in the future to see the influence of microRNAs on the global dynamics of the
metabolic networks involving proteins like pb1, when their interaction graphs will
be better known (Koparde and Singh
2010
; Cullen
2010
; Wang et al.
2009
).
We will give indications in Sect.
4.6
about the way to study the attractors of the
networks reduced to their strong connected components, which are circuits of genes
isolated, tangential or intersected, on which calculations about the number and
nature of their attractors can be possible.

















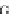


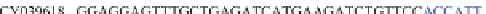












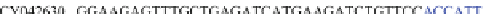
























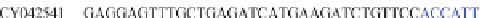
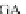









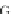


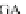




Search WWH ::

Custom Search