Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
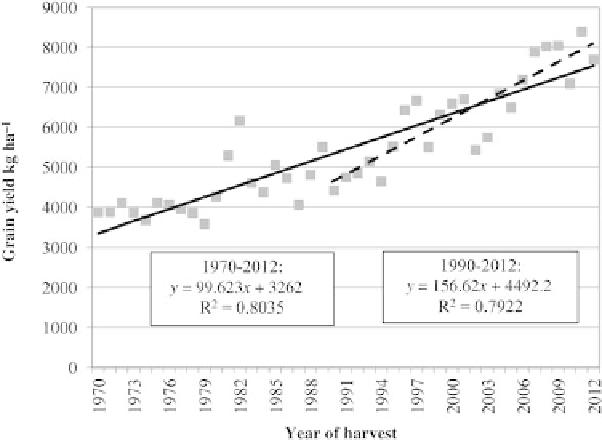
Fig. 5.3.
Average rice grain yield in Uruguay between 1970 and 2012 (harvest year).
2. Evolution of Grain Yield.
Between 1931 and 1970, grain yield was
relatively low and stable, with an average of 3.25 t ha
1
. As a result of the
adoption of improved cultivars and cultural practices, grain yield has
been increasing since 1970, achieving a maximum of 8.4 t ha
1
in 2010
-
2011. National average grain yield increased at a rate of 100 kg ha
1
per
year between 1970 and 2012, and at 157 kg ha
1
per year between 1990
and 2012 (Fig. 5.3). Between 1971 and 1990, the national average yield
increased by 36% (average for 5 years), driven by the adoption of
introduced variety Bluebelle and by improved cultural practices. The
replacement of Bluebelle by the high-yielding cultivars El Paso 144,
INIA Tacuarí, and INIA Olimar, and further improvement in cultural
practices, resulted in a 67% grain yield increase between 1990 and 2012
(Blanco et al. 2010). Further increases in rice productivity, however, will
be dif
cult to obtain, because the average grain yield obtained by farmers
70%of the environmental yield potential (10.9 t ha
1
) (Pérez de Vida
2010). The massive adoption of cultural practices by farmers makes grain
yield variation closely related to weather variability, mostly incident
radiation and temperature regimes (Pérez de Vida 2011).
is
∼
3. Rice Cultivars.
Between 1971 and 1990, production was dominated
by the U.S. variety Bluebelle, which replaced several
introduced