Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
C
Intraprocedural
DFA
Specification
c
0
Intraprocedural
Theory
Practice
DFA
Framework
Generator
Generic
Fixed Point Alg.
Intraprocedural
Termination
Lemma
Intraprocedural
Intraprocedural
Program
Property
φ
Equivalence
Coincidence Theorem
Correctness Lemma
Computed Solution
MOP-Solution
MFP-Solution
Proof
Obligations:
2
1
3a)
3b)
Equivalence
Coincidence
Effectivity
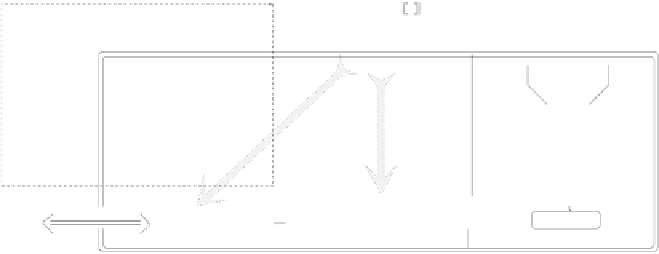
Fig. 3.
The intraprocedural DFA generator.
Following the pattern of Figure 3 the solution of the DFA problems for up-
safety and down-safety, which have informally been dened in Section 3.1, reduce
to providing the intraprocedural DFA generator with the appropriate specica-
tions of these two properties.
Computing Up-safety and Down-safety.
Let
denote the set of Boolean
truth values
true
and
false
, and let
Cst
true
,
Cst
false
,and
Id
B
denote the constant
functions and the identity on
B
B
. Then, the specications for the up-safety and
down-safety problem for
t
are as follows.
1.
Up-safety
:
(a)
Data-flow facts
:(
C;u;v;?;>
)=
df
(
B ; ^ ; ;
false
;
true
)
(b)
Data-flow functions
:[]
us
:
E !
(
B!B
) dened by
<
Cst
true
if
Comp
e
^
Transp
e
8 e 2 E:
[[
e
]]
us
=
df
Id
B
if
:
Comp
e
^
Transp
e
:
Cst
false
otherwise
(c)
Start assertion
:
false
2B
2.
Down-safety
:
(a)
Data-flow facts
:(
C;u;v;?;>
)=
df
(
B ; ^ ; ;
false
;
true
)
E !
B!B
(b)
Data-flow functions
:[]
ds
:
(
) dened by
8
<
Cst
true
if
Comp
e
:
Comp
e
^
8 e 2 E:
[[
e
]]
ds
=
df
Id
B
if
Transp
e
:
Cst
false
otherwise
(c)
Start assertion
:
false
2B











Search WWH ::

Custom Search