Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
ment has chosen so far not to add this capability to the CS.) As stated previously, the
primary and secondary SV payloads are navigation and NUDET, respectively.
Occasionally, the satellites carry additional payloads, such as laser reflectors for
satellite laser ranging (i.e., validation of predicted ephemeris), and free electron
measurement experiments.
3.2.3.3 Block I—Initial Concept Validation Satellites
Block I satellites were developmental prototypes to validate the initial GPS concept,
so only 11 satellites were built. The Block I satellites, built by Rockwell Interna-
tional, were launched between 1978 and 1985 from Vandenberg Air Force Base,
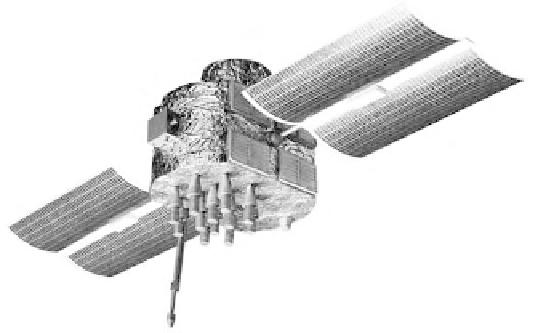
California. A picture of the Block I satellite is presented in Figure 3.4. The onboard
storage capability was for about 3.5 days of navigation messages. The navigation
message data was transmitted for a 1-hour period and was valid for an additional 3
hours. Since there was no onboard momentum dumping, frequent ground contact
was required for momentum management. Without momentum dumping, the satel-
lites would lose attitude control after a short time interval. Two cesium and two
rubidium AFSs were employed. These satellites were designed for a mean mission
duration (MMD) of 4.5 years, a design life of 5 years and inventory expendable
(e.g., fuel, battery life, and solar panel power capacity) of 7 years. Reliability
improvements were made to the atomic clocks on later satellites based on failure
analysis from earlier launches. Some Block I satellites operated for more than double
their design life.
3.2.3.4 Block II—Initial Production Satellites
On-orbit operation of the Block I satellites provided valuable experience that led to
several significant capability enhancements in subsystem design for the Block II
operational satellites. These improvements included radiation hardening to prevent
random memory upset from such events as cosmic rays to improve reliability and
survivability. Besides these enhancements, several other refinements were incorpo-
rated to support the fully operational GPS system requirements. Since the NDU pro-
cessor would not be programmable on-orbit, flexibility was designed into the flight
Figure 3.4
Block I satellite.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search