Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
11.1.5 Spacecraft Description
The Russians are currently populating the GLONASS constellation with two types
of spacecraft, the original GLONASS satellite-series design and the new
GLONASS-M satellite-series design. Within each series, there are different blocks
that denote subtle changes in the spacecraft payloads and electronics. These changes
were introduced to increase satellite lifetime [9-12].
11.1.5.1 GLONASS
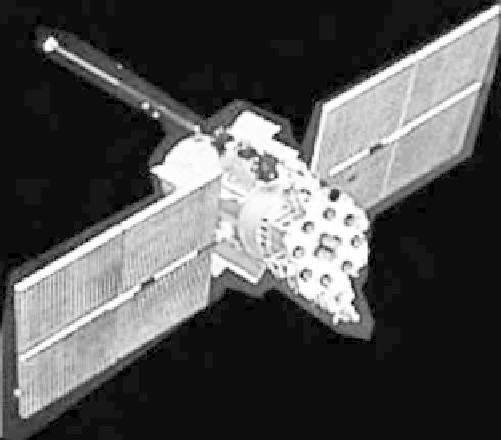
From 1982 through 2005, the Russians planned to launch GLONASS series satel-
lites. This satellite is a traditional Russian design consisting of a pressurized, her-
metically sealed cylinder that is three-axis stabilized (i.e., oriented in all three axes
of motion, usually measured as in-track, cross-track, and radial from the satellite's
point of view). Circulation of gas inside the pressurized vessel allows for cooling of
the satellite electronics. Attached to the bottom of the spacecraft is the payload
assembly. This assembly consists of the horizon sensor, laser retroreflectors, a
12-element navigation signal antenna, and various command and control antennas.
Attached to the sides of the pressurized cylinder are the solar panels, orbital correc-
tion engines, a portion of the attitude control system, and the thermal control
louvers [1]. A GLONASS satellite is shown in Figure 11.2.
Within the original GLONASS series, there have been two major block changes
(referred to as types I and II by the Russians) and three variants (referred to as a, b,
and c) within the second block. The main difference between the spacecraft blocks is
the design lifetime. Early satellites had design lifetimes of 1 to 2 years. At the time of
this writing, the Russians were launching GLONASS type IIc spacecraft with a
3-year design lifetime. A tabulation of the GLONASS satellites, their respective
orbital locations, and frequency assignments is contained in Table 11.1. Unlike
GPS, which transmits CDMA format, GLONASS employs frequency division mul-
tiple access (FDMA) [1]. (Details on this scheme are provided in Section 11.1.9.)
Figure 11.2
GLONASS satellite.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search