Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
GPS Rx
123
456
789
Assist server
Over-the-air standards protocol
Position
server
-
-
MS-based
MS-assisted
Ephemeris, approx position
and time, almanac, DGPS
real-time integrity,
sensitivity assist
SVIDs, Dopplers,
code phases,
AZ/EL,
sensitivity assist
Handset
inputs
Measured code
phases, measured
Dopplers, C/N s
Position, velocity, time,
quality, error ellipse
Handset
outputs
0
Position
computed
In handset
In network
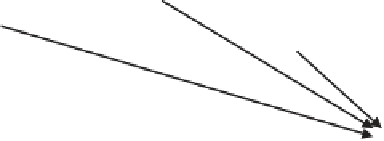
Figure 9.35
Assisted GPS positioning methods.
from the GPS reference network are transmitted to the mobile phone GPS sensor to
aid fast start-up and to increase the sensor sensitivity. Acquisition time is reduced
because the Doppler and code phase uncertainty space is much smaller than in con-
ventional GPS because the search space has been predicted by the network. This
allows for rapid search speed and for a much narrower signal search bandwidth,
which enables enhanced sensitivity by allowing the receiver to dwell longer in each
of the reduced Doppler/code phase uncertainty cells. Once the embedded GPS sen-
sor acquires the available satellite signals, the pseudorange measurements can be
delivered to a network-based PDE or used internally to compute position in the
handset.
Additional assistance data, such as DGPS corrections, approximate handset
location or cell BS location, and other information such as the satellite ephemeris
data and clock correction can be transmitted to improve the location accuracy,
decrease acquisition time, and allow for handset-based position computation. Sev-
eral schemes have been proposed in the standards that reduce the number of bits
necessary to be exchanged between the handset and the network by using compres-
sion techniques such as transmitting only the changes to parameters instead of the
raw parameters themselves. Other satellite systems could be used, such as the Rus-
sian GLONASS system (see Section 11.1), but current standards only provide for
GPS and WAAS (see Section 8.6.1.2) signals. Besides adding a GPS reference net-
work and additional location determination units in the network, the mobile phone
must embed, at a minimum, a GPS antenna and RF downconverter circuits, as well























Search WWH ::

Custom Search