Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
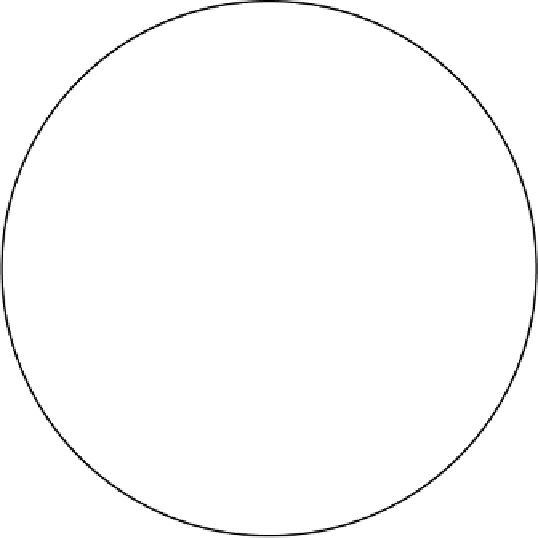
Foghorn 1
R1
Figure 2.1
Range determination from a single source. (
After:
[1].)
Hypothetically, if the mariner simultaneously measured the range from a second
foghorn in the same way, the vessel would be at range
R
1 from Foghorn 1 and range
R
2 from Foghorn 2, as shown in Figure 2.2. It is assumed that the foghorn transmis-
sions are synchronized to a common time base and the mariner has knowledge of
both foghorn whistle transmission times. Therefore, the vessel relative to the fog-
horns is at one of the intersections of the range circles. Since it was assumed that the
mariner has approximate knowledge of the vessel's position, the unlikely fix can be
discarded. Resolving the ambiguity can also be achieved by making a range mea-
surement to a third foghorn, as shown in Figure 2.3.
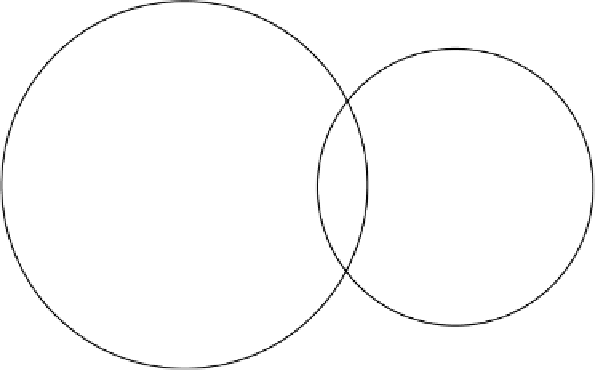
Ambiguity: vessel
can either be at
point A or point B
A
Foghorn 1
Foghorn 2
R2
R1
B
Figure 2.2
Ambiguity resulting from measurements to two sources. (
After:
[1].)




Search WWH ::

Custom Search