Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
Estimated horizontal
position error
Slope
max
Miss rate
Horizontal
integrity
limit
T
D
pbias
Test statistic |p|
Figure 7.23
Scatter plot with critical bias on Slope
max
satellite.
to the left, increasing the missed detection rate beyond the allowable limit. This criti-
cal bias value in parity space is denoted as pbias. The pbias term is completely deter-
ministic, but it is dependent on the number of visible satellites [43]:
pbias
= σ
λ
UERE
where
λ
is the noncentrality parameter of the noncentral chi-square density function,
and
σ
UERE
is the standard deviation of the satellite pseudorange measurement error.
The HPL is determined by
HPL
=
Slope
max
×
pbias
When SA was the dominant error source, other error terms that depend heavily
on the elevation angle were negligible. For this reason, pre-2000 RAIM and FDE
availability analyses typically assumed a fixed
σ
UERE
value of 33.3m for all satellites,
regardless of the satellite elevation angles. Now that SA has been discontinued,
errors that depend on the elevation angles make
σ
UERE
values for each satellite signifi-
cantly different.
Accounting for elevation-dependent errors is accomplished through weighting
(or deweighting) of individual satellite range measurements [46]. The only differ-
ence between the weighted solution RAIM and the nonweighted solution RAIM is
the formula for the maximum horizontal slope, which is shown next.
The threshold and pbias values are the same as with SA on. This is because the
maximum false alarm rate is set at 0.333
10
−6
/sample, which is consistent with the
×
guidance in [14] for SA off.
()
2
2
SLOPE
i
=
AA
+
σ
S
1
i
2
i
i
ii
where:
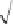








Search WWH ::

Custom Search