Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
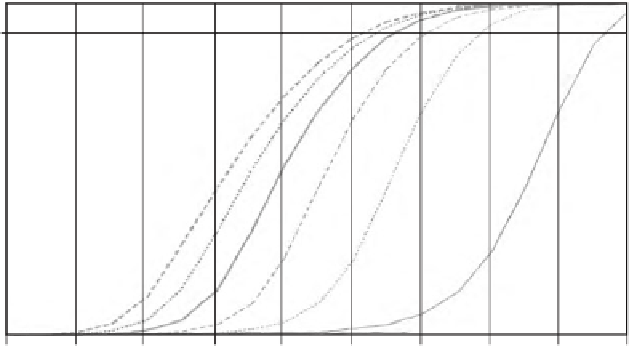
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
A=10
Mean cell time = 1.57
A=8
Mean cell time=1.33
A=12
Mean cell time = 1.83
A=6
Mean cell time =1.14
40%
30%
20%
A=4
Mean cell time =1.02
A=2
Mean cell time =1.00
10%
0%
−
4
−
2
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
−
C/N (dB) into envelope detector with P
= 10
FA
Figure 5.38
Probability of detection for Tong search detector.
with the increase of
A
. The cost of increasing
A
is shown as a decrease in the search
rate.
5.8.2
M
of
N
Search Detector
The second example of a search algorithm is a fixed interval detector called the
M
of
N
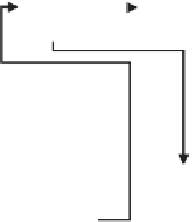
search detector. Figure 5.39 depicts the
M
of
N
search algorithm. The
M
of
N
search detector takes
N
envelopes and compares them to the threshold for each cell.
If
M
or more of them exceed the threshold, then the signal is declared present. If not,
the signal is declared absent, and the process is repeated for the next cell in the
search pattern. These are treated as Bernoulli trials, and the number of envelopes,
n
,
that exceed the threshold has a binomial distribution. The same threshold-setting
technique is used and the same formula applies for the single trial probability of
Declare
signal
present
Yes
J=J+1
J
≥
M?
No
Yes
I
Q
Envelope
detector
−
Continue
in same cell
COMP
Env>V ?
t
+
V
threshold
t
No
No
Declare
signal not
present
Yes
K=K
−
K=0?
Recursive
lowpass
filter
Scale
factor
Q
N
N
i
m
=
∑
1
N
SetJ=0
SetK=N
and move
to next cell
Q
n
Q
R
σ
n
Figure 5.39
M
of
N
(fixed interval) sequential code search algorithm.




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search