Global Positioning System Reference
In-Depth Information
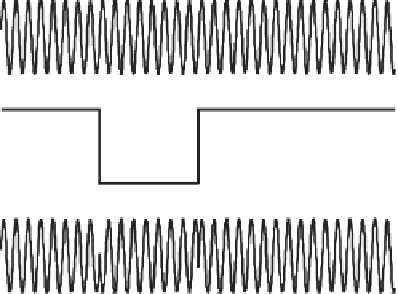
RF carrier
1
+
Data waveform
×
−
1
T
b
BPSK signal
=
Figure 4.1
BPSK modulation.
rection
(FEC) is employed, whereby redundant bits (more than the original informa-
tion bits) are transmitted over the channel according to some prescribed method,
enabling the receiver to detect and correct some errors that may be introduced by
noise, interference, or fading. When FEC is employed, common convention is to
replace
T
b
with
T
s
and
R
b
with
R
s
to distinguish data symbols (actually transmitted)
from data bits (that contain the information before FEC). The data waveform alone
is considered a
baseband
signal, meaning that its frequency content is concentrated
around 0 Hz rather than the carrier frequency. Modulation by the RF carrier centers
the frequency content of the signal about the carrier frequency, creating what is
known as a
bandpass
signal.
Direct sequence spread spectrum
(DSSS) is an extension of BPSK or other phase
shift keyed modulation used by GPS and other satellite navigation systems discussed
in this text. As shown in Figure 4.2, DSSS signaling adds a third component, referred
to as a
spreading
or PRN waveform, which is similar to the data waveform but at a
much higher symbol rate. This PRN waveform is completely known, at least to the
intended receivers. The PRN waveform is often periodic, and the finite sequence of
bits used to generate the PRN waveform over one period is referred to as a
PRN
RF carrier
1
+
Data waveform
×
1
−
+
1
Spreading
waveform
×
−
1
T
c
DSSS signal
=
Figure 4.2
DSSS modulation.






Search WWH ::

Custom Search