Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
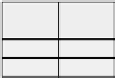
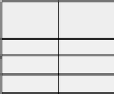
Peer 2 Transaction Record Table
Remote
Peer ID
Remote Peer's
Trust Score
Transaction
Amount
Transaction
Date
Global Aggregation
Weight
4
0.5
$15
02/11/2005
0.5
9
0.7
$10
02/15/2005
0.6
20
0.9
$99
02/13/2005
0.8
28
0.8
$399
02/14/2005
0.9
Peer 2
Peer 4
Peer 28
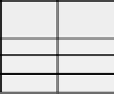
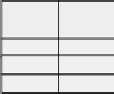
Peer 28 Score Table
Peer 4 Score Table
Remote
Peer ID
Local
Score
Remote
Peer ID
Local
Score
2
0.9
2
0.7
4
0.7
...
...
Peer 9 Score Table
Peer 20 Score Table
Remote
Peer ID
Local
Score
Remote
Peer ID
Local
Score
2
0.6
2
0.7
16
0.8
16
0.9
...
...
Peer 20
Peer 9
Peer 16
Peer 16 Transaction Record Table
Remote
Peer ID
Remote Peer's
Trust Score
Transaction
Amount
Transaction
Date
Global Aggregation
Weight
20
0.9
$5
02/01/2005
0.5
9
0.8
$100
02/15/2005
0.9
FIGURE 6.8: Illustrative example of FuzzyTrust [Song et al., 2005].
of trust but rather it is a belief that a peer will act against the best interests
of another. Alternatively, untrust corresponds to the space between distrust
and trust, in which an agent is positively trusted, but not to the extent that
it warrants full cooperation. This view of trust was originally advocated by
Marsh and Dibben [Marsh and Dibben, 2005]. Inspired by this definition,
Gri
ths et al. suggested a novel concept called undistrust.
According to Gri
ths et al., a similar region of undistrust is needed,
namely negative trust, but insu
cient to make definite conclusions in the
trust reasoning process.
Figure 6.10(b) illustrates their definition of the notions of trust, distrust,
untrust, and undistrust.
Preliminary results presented in [Gri
ths et al., 2006] indicated that the








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search