Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
system that is suitable for a P2P computing environment. Specifically, they
defined a practical trust model suitable for a P2P computing environment.
Trust Agent
(TA)
Trust Agent
(TA)
Domain (D)
Domain (D)
Recommendation
Trust Agent
(TA)
Domain (D)
Set of Recommenders
Source
Domain
(SD)
Target
Domain
(TD)
Trust Agent
(TA)
Trust Agent
(TA)
Resource
Domain
(RD)
Client
Domain
(RD)
Resource
Domain
(RD)
Client
Domain
(RD)
Direct
Relationship
FIGURE 6.1: Trust model for a generic P2P computing system [Azzedin
and Maheswaran, 2003].
Figure 6.1 depicts the trust model for a P2P system. The model is parti-
tioned into domains (denoted as D's). There are two virtual domains associ-
ated with each D: (1) a resource domain (RD) to signify the resources within
the D; (2) a client domain (CD) to signify the clients within the D. Trust
agents (TAs) are designated in each D. Each TA has the following functions:
•update the D's trust tables;
•allow entities to join D's and inherit their trust attributes; and
•apply a decay function to reflect the decay of trust between D's.
Each D maintains two data structures: DTT and RTT, which are updated by
the TA. The DTT is updated using the trust values observed based on the
direct transactions with other D's. The RTT is updated by monitoring the
accuracy of recommendations given about target D's.
To illustrate the trust modeling, suppose that an RD in a source domain
(SD) is about to establish a trust relationship with a CD associated with a
target domain (TD). The SD gathers information to build its direct relations
by obtaining its direct relationship TL to TD from its DTT which is internal
to the SD. The SD can obtain the reputation value of TD by asking its R.
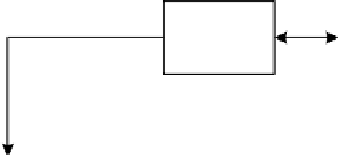
Figure 6.2 shows a recommendation network that enables the establishment
of a trust relationship. Each member z∈R provides recommendations based
on its DTT. If TD is unknown to recommender z, then z will ask its R. To






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search