Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
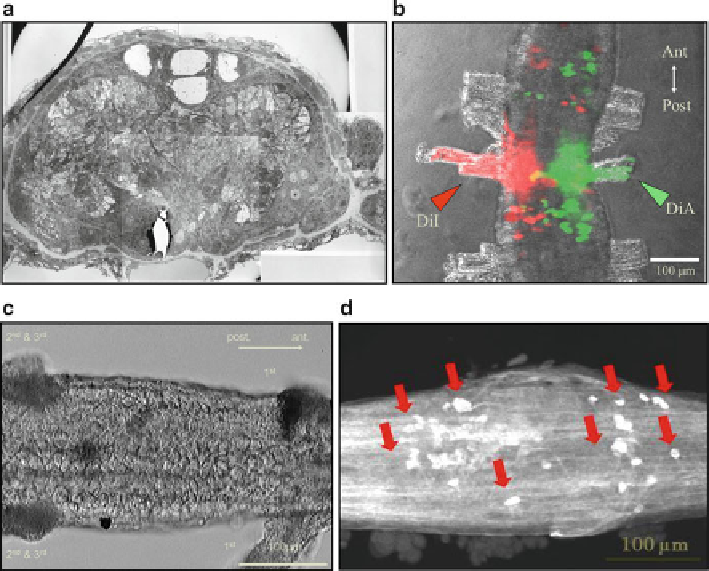
Fig. 6.2
Several types of imaging techniques that are useful for neuroethological studies. (
a
) Cross
section of the ventral nerve cord (VNC) of the earthworm. MGF and a pair of lateral giant fi bers
(LGFs) are observed on the dorsal side. Cell bodies of neurons with huge nuclei are located in the
peripheral region of the VNC. (
b
) Retrograde trace of neurons using lipophilic fl uorescent dyes
(DiI and DiA). Two different dyes were applied to the right and left cut ends of the fi rst segmental
nerves, and the cell bodies of the projection neurons are imaged with
red
and
green color
s. In the
middle part of the VNC, a yellow-colored neuron indicates a projection neuron to both the right
and left segmental nerves. (
c
) Differential interference contrast microscopy with infrared illumina-
tion. This method is useful for inserting a microelectrode into specifi c neurons without staining.
(
d
) Immunohistochemistry of the VNC using an anti-serotonin antibody. This old method has been
revived following the development of several new fl uorophores for multicolor staining
Finally, we do not forget the use of conventional immunohistochemistry
(Fig.
6.2d
). In this fi gure, neurons containing the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-HT)
are visualized. Although this is an old technique, a combination of this technique
and other imaging and/or electrophysiology methods is fundamental for neuroetho-
logical investigations characterizing specifi c neurons. In the ventral nervous system
of the earthworm, we found specifi c neurons with two neurotransmitters, 5-HT and
FMRF amide, that control the circular and longitudinal muscles, respectively. These
specifi c neurons are important for the coordinated contraction of muscles during
locomotion.