Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
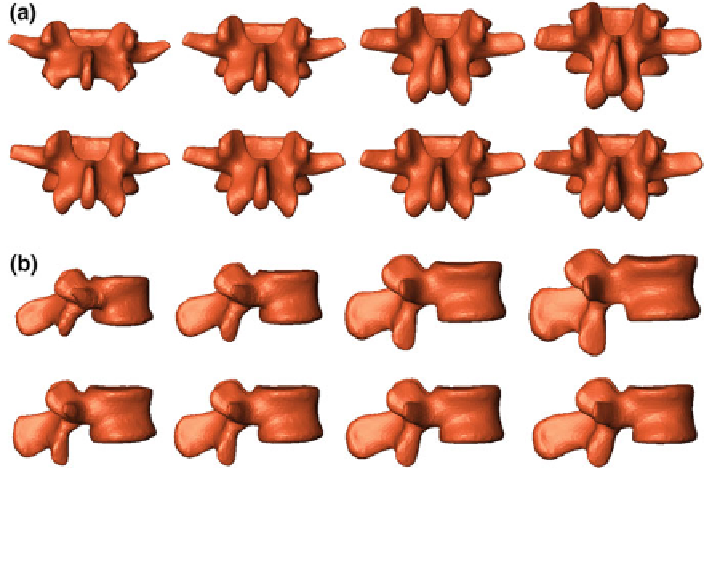
Fig. 1 The
first two principal modes of variation of the PDM used in this investigation. The shape
instances from left
to right at each row were generated by evaluating
x
þ ar
k
p
k
;
a 2
f
with (a) Posterior view of the PDM (k = 1: the 1st row; k = 2: the 2nd row);
and (b) Lateral view of the PDM (k = 1: the 1st row; k = 2: the 2nd row)
2
;
1
;
1
;
2
g
[
20
,
21
], where two or more calibrated X-ray images were required as the input for
a successful reconstruction, here only a single lateral
fluoroscopic image is avail-
able. Similar to the situation when multiple images are used, the convergence of the
single image based 2D/3D reconstruction also depends on the initialization and on
the image contour extraction. Thus, in the following we focus on the image contour
extraction and on a landmark-based scaled rigid registration for initializing the
single image based 2D/3D reconstruction.
fl
3.1 Image Contour Extraction
As a feature-based 2D/3D reconstruction approach, our technique requires a pre-
requisite image contour extraction. Explicit and accurate contour extraction is a
challenging task, especially when the shapes involved become complex or when the
background of the image becomes complex. In this paper, we feel that it is a far better
choice to provide the user with a tool that supports interactive segmentation but at the
same time speeds up the tedious manual segmentation process and makes the results
repeatable. This leads us to developing a semi-automatic segmentation tool.
Our semi-automatic segmentation tool is based on the Livewire algorithm
introduced by Mortensen and Barrett [
26
]. In their paper, graph edges are de
ned as