Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
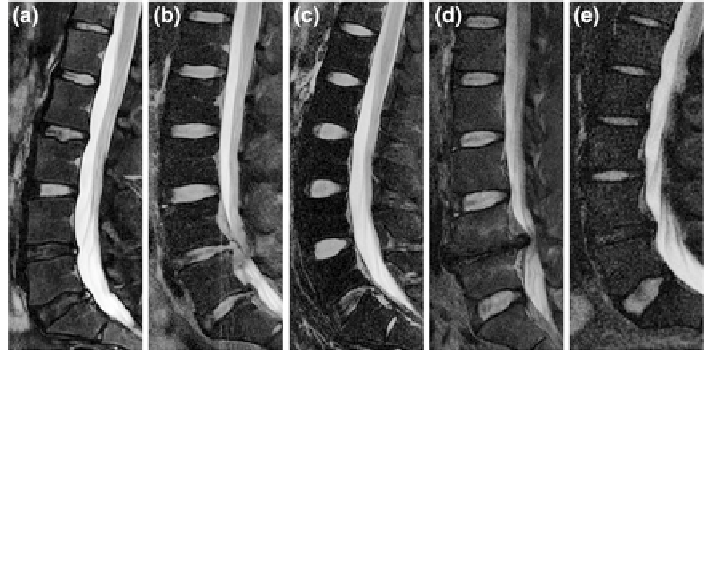
Fig. 13 Variability in disc appearances, shapes, locations, and sizes in different abnormal cases.
a Shows variability in appearance of discs. The lower two discs (L4-L5 and L5-S1) have less
intensity levels due to abnormalities (Herniation, Stenosis and Desiccation). b Shows variability in
shape of discs with close intensity levels due to abnormalities in the lower two discs (Herniation
and Stenosis). c Shows clear difference at the lowest disc level (L5-S1) as well as the difference in
bending of the lumbar vertebral column which results in variability in location. d Shows variability
in location of discs from other
figures, sizes of discs, and the missing disc at L4-L5 disc. e Shows
variability in disc sizes between the upper four discs and the lowest disc L5-S1. Ages of these
patients are 35, 36, 29, 47, and 27, respectively from a to e. All images have been edited by
cropping and contrast enhancement for better visualization
5 Advances in Localization, Labeling, and Segmentation
There are three main steps for the proper diagnosis in medical imaging: (1)
Localization and labeling of anatomic structures, (2) Segmentation and (3) Diag-
nosis and quanti
cation of abnormalities. There has been an extensive amount of
work done in the area of vertebral body localization and segmentation from X-ray
radiographs and CT scans in the past two decades. On the other hand, localization
of soft tissues in MRI and diagnosis of disc abnormalities is comparatively more
recent and has been of central focus for low back research in the last decade.
In this section, we review in detail, the current literature in the context of spinal
tissue localization, segmentation and abnormality diagnosis. We classify the liter-
ature based on the medical imaging modality.