Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
4 Challenges
Automatic detection of abnormalities from MRI or CT scans has been studied by
researchers for quite some time. The challenges are manifold
—
ranging from
variations in scanner speci
cations, parameter settings, modalities, differences in
body structure and composition and last but not the least the task of segmentation
which is a big challenge in computer vision.
In general, the segmentation of CT and MRI scans is difficult due to three main
reasons.
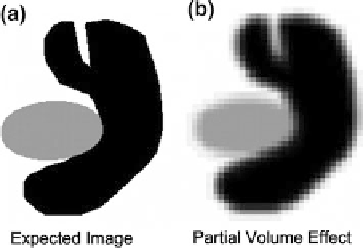
(1) Partial Volume Effect: It is a scenario where multiple tissues contribute to
pixels and blurs intensity across boundaries as illustrated in Fig.
10
.
(2)
Intensity Inhomogeneity:Itisde
ned as non-anatomic intensity variations of
the same tissue over the image, and may be caused by the imaging instru-
mentation (RF non-uniformity, static
field inhomogeneity) or due to patient
movement as seen in Fig.
11
.
(3)
Intensity Similarity: Very often two or more tissues have the same intensities
in MRI scans as illustrated in Fig.
12
.
All these factors contribute to the fact that segmentation of a lumbar MRI is a
very challenging task.
Real world clinical MRIs are even more challenging since patients very often
suffer from one or more lumbar abnormalities such as vertebral fractures, Spon-
dylolysis, Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis, intervertebral disc abnormalities (degener-
ation, desiccation, herniation, bulge and annular tears) and spinal Stenosis. In
addition, there is lumbar variability due to patient age, height and structure leading
to diverse images. Figure
13
shows a sample set of clinical lumbar MRIs showing
some of the variability [
5
].
Fig. 10 This figure shows an illustration of partial volume effect in an imaginary scan consisting
of two different kinds of tissues. While the first image shows the expected image the second one
shows the actual image with fuzzy boundaries due to partial volume effect [
32
]