Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
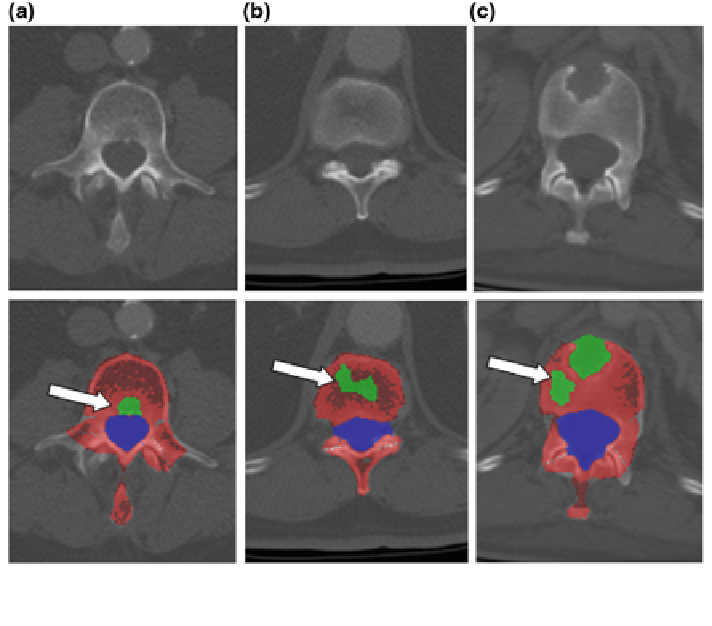
Fig. 10 False positive detections in lytic metastasis CAD. First row CT image; Second row false
positive detections. a Basivertebral vein; b vertebral disk; and c volume averaging
connections between the basivertebral vein and the anterior external venous plexus
(106, 34 % of FPs), (2)
, low intensity disks or volume averaging with disks
(83, 27 %), (3) Osteopenia (68, 22 %), (4)
“
Disk
”
“
Outside
”
, on areas outside the vertebra
(37, 12 %), (5)
“
Basivertebral vein
”
, which enters the posterior vertebral body (6,
2 %), (6)
, a drop in intensity from volume averaging with normal
structures such as joints or oblique cuts through the cortex (6, 2 %), and (7)
“
Normal
”
“
Spinal
canal
(2, 1 %). Two of the FP detections were actually on reference standard
lesions that were not segmented on all slices in which they appeared. False positive
detections varied greatly amongst patients, numbering 0 to 20 per patient (average
6.2). Some examples of FPs are shown in Fig.
10
. We also analyzed the 3 false
negative detections (FNs) (two in the training set, one in the test set). Two were in
pedicles that were not properly segmented, so they were never detected. The other
FN was initially detected, but thrown out by the classi
”
er, most likely due to
similarity to a basivertebral vein.