Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
10
0
10
1
10
2
Scaled inclusion radius,
a
/
x
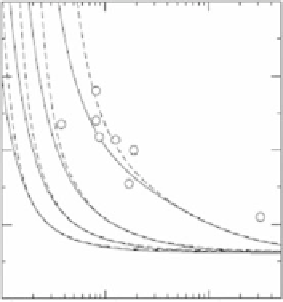
Figure 10.9
The scaled effective diffusivityD
e
/D
∞
versus the scaled inclusion radius a/
ξ
where D
e
the composite diffusivity, D
∞
=
=
the bulk diffusivity, a
=
the radius of the
nanoparticleinclusion,
ξ
=
0
.
8 nm, thethicknessof thedepletedzonearoundtheinclusion.
The circles are experimental measurements of the permeability enhancement fromMerkel
etal.(Merkeletal.2002).GraphfromHill(Hill2006b).
100
90
50 m
2
/g
100 m
2
/g
200 m
2
/g
300 m
2
/g
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
% filler content
Figure10.10
Simpleestimateoftheamountofthepolymermatrixresidingintheinterphase
asafunctionoffillersurfaceareaandcontent.
have more or less free volume than the bulk matrix and may therefore exhibit different
transport properties.
We have observed the dependence of water vapor transport on CNXL content in
different polymer systems: CMC (not shown here), PSf, and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVOH)
(Figure 10.11).
The CMC, filled with 5% CNXLs, showed very high water vapor










































Search WWH ::

Custom Search