Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
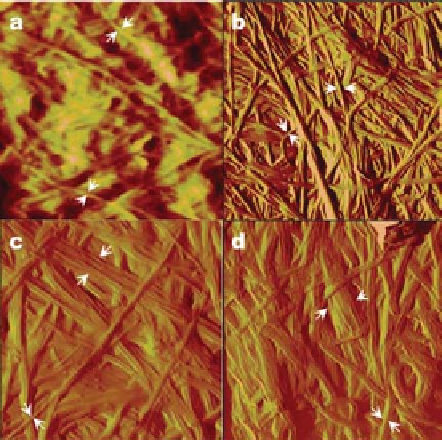
Figure 9.27
Atomic Force Microscopy Images of BC grown in (a) HS medium, (b) HS
mediumwith 1% PEO, (c) HS medium with 3% PEO, and (d) HS mediumwith 5% PEO
(68).(ReprintedwithpermissionfromBrown,E.E.;Laborie,M.-P.G.,Bioengineeringbacterial
cellulose/poly(ethylene oxide) nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules, 2007, 8, 3074-81.
Copyright(2007),AmericanChemicalSociety.)
10
9
10
8
10
7
59:41
53:47
33:67
23:77
15:85
0:100
10
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
−
60
−
40
−
20
0
Temperature (
20
40
60
80
100
°
C)
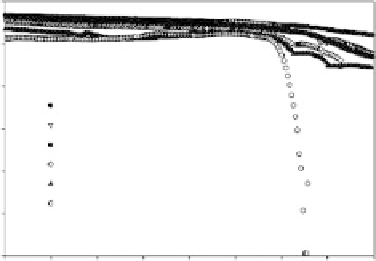
Figure 9.28
Storage tensile modulus E' versus temperature at 1 Hz for nanocomposites
of varying BC/PEO ratios (68). (Reprinted with permission from Brown, E.E.; Laborie,
M.-P.G.,Bioengineeringbacterialcellulose/poly(ethyleneoxide)nanocomposites.Biomacro-
molecules,2007,8,3074-81.Copyright(2007),AmericanChemicalSociety.)
various water-soluble polymers including poly(vinyl alcohol). It appeared that PVA was
easily washed from the BC/PVA nanocomposite during the purification step although
some PVA could be detected when 2% PVA was added in the growth medium of BC. In
this case, the BC network structure and crystalline structure appeared to be unaffected by
the presence of PVA. This contrasted with the morphology of the BC/methyl cellulose
Search WWH ::

Custom Search