Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table7.2
(continued).
Bond
Chemical structure
Percentage of total bond linkages
Softwood
Hardwood
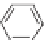
4-O-5
4
7
OH
O
MeO
OH
MeO
β
-1
7
7
OMe
HO
O
OMe
OH
β
-
β
2
3
O
MeO
HO
OMe
OH
all inter-unit bonds in the lignin macromolecule and this bond is particularly susceptible
to nucleophilic attack, a fact which is exploited in the kraft pulping process (Gellerstedt
and Lindfors 1984).
7.3
Isolation of Lignin from Wood, Pulp and Pulping Liquors
In 1838, the Frenchman Anselme Payen treated wood with nitric acid followed by an
alkaline solution. Payen discovered that some of the wood dissolved by this procedure
had a higher carbon content than the insoluble fibrous material; 'la matiere incrus-
tante'. This material was nineteen years later designated lignin by the German scientist
F. Schulze. In 1890 the Swede Peter Klason found an analytical method based on treat-
ment with strong sulphuric acid to determine the lignin content in wood. In 1897 he
studied lignin's composition in sulfite spent liquors and found that it was chemically
related to coniferyl alcohol. Somewhat later Klason also proposed that lignin was a
macromolecular substance and that the coniferyl alcohol units were coupled together

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search