Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.13
An XSD graph for
a disjoint generalization
Librarian
d
ContractStaff
(extension)
PermanentStaff
(extension)
Rule 8 A circle with a letter “c” means categorization such that each subclass
element instance is in an isa relationship with one of the multiple superclasses ele-
ments' instances.
For example, the following is an XSD for a disjoint generalization such that a staff
can either be a contract staff or a permanent staff:
³
´
´
´
³
³
´
´
³
³
Its corresponding XSD graph is shown in Fig.
2.13
.
2.6
Expert System
An expert system (ES) has been seen as an important information system for organi-
zations in recent years. It is a piece of software that seeks to model the expertise of a
human expert within a specific narrow problem domain. It has a comparatively short
history under the aegis of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The early period of AI was
dominated by the brief that a few general problem-solving strategies implemented
on a computer could produce expert level performance in a particular domain. As
AI was developed, it was soon realized that such general-purpose mechanisms were
too weak to solve the most complex problems. In reaction to these limitations, users
began to concentrate on more narrowly defined problems, and expert systems were
developed.
An ES generally consists of five parts (see Fig.
2.14
):
• Inferenceengine:Thecomponentofthesystemthatusestheknowledgebaseto
respond to queries posed by users.
• Knowledgebase:Therepositoryofdomain-specificknowledge.


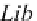

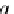
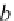
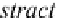



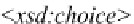





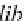
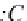
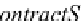


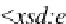



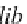
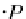

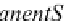












Search WWH ::

Custom Search