Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
5(&25'
&/$66
5(&25'
/(&785(5
(17,7<
&/$66
(17,7<
/(&785(5
6(&7,21
0
1
VHW
VHW
1
1
$77(1'('%<
5(&25'
6(&7,21
VHW
1
1
(17,7<
678'(17
5(&25'
678'(17
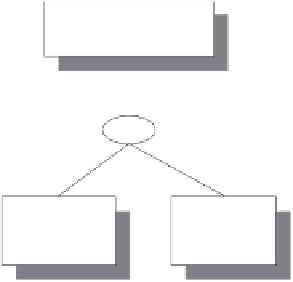
1HWZRUN6FKHPD
7UDQVODWHG((5PRGHO
Fig. 3.9
Map set of relationships to aggregation in EER model
(03/2<((
(03/2<((
SDLGVFDOH
VHW
VHW
G
6DODULHG
HPSOR\HH
+RXUO\
HPSOR\HH
6DODULHG
HPSOR\HH
+RXUO\
HPSOR\HH
1HWZRUN6FKHPD
FRUUHVSRQGLQJ((5PRGHO
Fig. 3.10
Map isa relationships to disjoint generalization
knowledge acquisition system should be able to detect such potential generalization
by locating isa relationship linkages with one owner and more than one member re-
cord type. However, user input is needed to confirm this. Figure
3.10
is an example
with Paid-scale used as an attribute in Employee entity to determine of which sub-
class (salaried-employee, hourly-employee) the superclass (Employee) is a member.
An overlap generalization is derived by mapping isa relationships and their re-
cord types to a superclass/subclass relationship such that a superclass entity (mapped
from an owner record type) is a generalized class for the subclass entities (mapped
from member record types) that overlap each other. Again, the knowledge acquisi-













Search WWH ::

Custom Search