Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
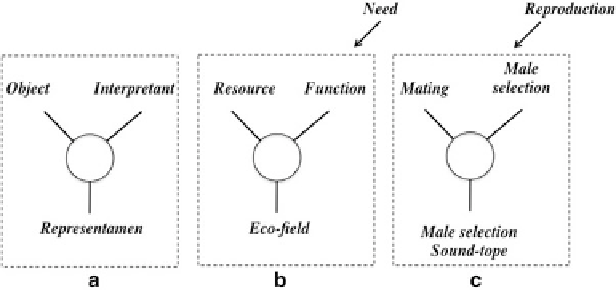
Fig. 1.13
The triadic structure of the segnic process according the Percian semiotic interpretation is
utilized to confirm the eco-field hypothesis. (
a
) The three components of the segnic process (object,
interpretant
,
representamen
) concur with the segnic process. (
b
) The eco-field hypothesis has been
explained using the Percian triadic sign process wherein is the need to initiate the segnic process.
Resources are located as a result of the identification of a spatial configuration carrier of meaning
(the eco-field) using a function as
interpretant
.(
c
) An example of mating (object-resource), male
selection soundtope (
representamen
-eco-field), and male selection (
interpretant
-function)
The sonic eco-field may be represented by a spatial arrangement of contempo-
rary coordinated vocalizations or soundtopes and in this case can be utilized to
evaluate density of individuals, richness of the composing community, or intra- and
interspecific competition.
The theory of the eco-field can be used to explain the function of the soundtope
that can be defined as a set of sonic eco-fields utilized for tracking resources such as
mating or food location.
For instance (Fig.
1.13c
), the “resource” is represented by the “mating,” the
(behavioral) “function” is represented by “male selection,” and the “eco-field” is
represented by the “male-selection soundtope.”
The activity-centric standpoint of Jennings and Cain (
2013
) is very close to the
idea of the sonic eco-field, but the arguments considered by these authors do not
consider the theory of resources and the eco-field hypothesis.
1.14 Landscape Fragmentation and Soundscape Processes
Population decrease is generally caused by the fragmentation and rarefaction of
habitats under a growing worldwide human impact. Fragmentation is one of the most
common causes of habitat degradation and species extinction. Small and isolated
populations are under a stronger pressure of extinction than large populations,
mostly dependent on inbreeding depression, demographic stochasticity, genetic
drift, and Allee effect. In social animals in particular, reduction of population
size curtails cultural transmission and large group cooperation.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search