Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
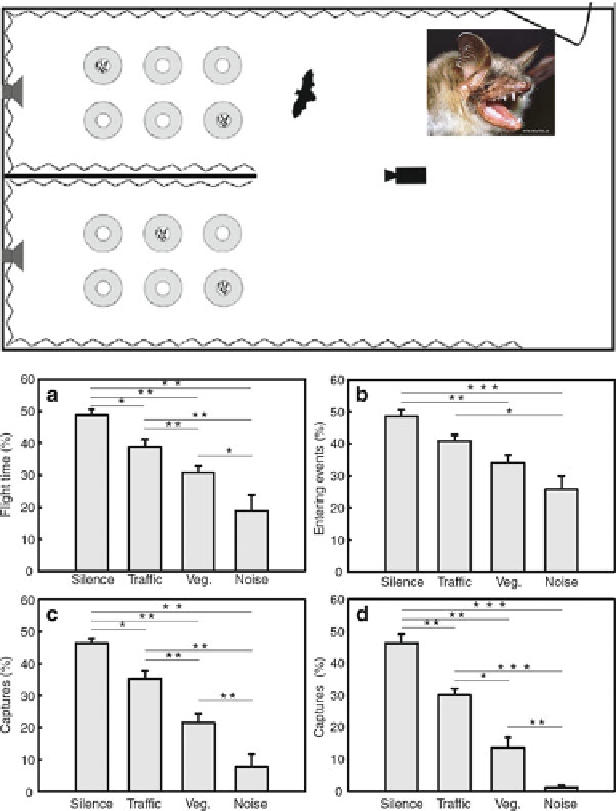
Fig. 6.13
Experimental flight room in which individuals of
Myotis myotis
were offered
mealworms in a silent and a noise compartment. Flight time (
a
), entering events (
b
), capture
(
c
), and percentage of the first 25 capture events (
d
) are compared with different sonic environ-
ment: silence, traffic, vegetation noise, broadband computing noise (Reproduced with permission
from Schaub et al.
2008
)
In marine coastal habitats, biological and abiotic noise is present at a high level.
For instance, the recent diffusion of offshore wind farms have all the potentiality to
modify the sonic ambience around the windmills, producing, as observed by
Wahlberg and Westerberg (
2005
), a displacement of fishes that avoid close contact
with these devices. This effect largely depends on wind speed, which generates
noise on the blades.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search