Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
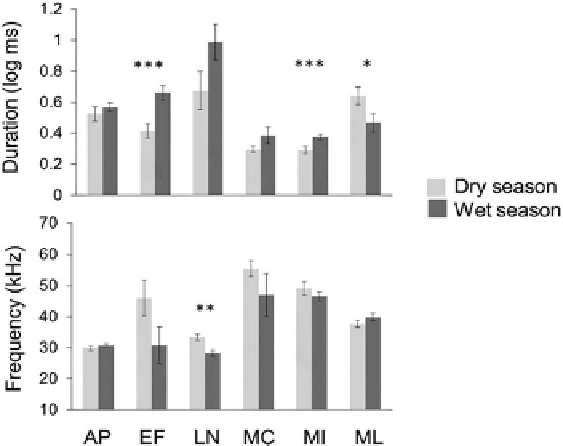
Fig. 4.13
Change in frequency and duration of calls of six species of bats during dry and wet
season: AP
Antrozous pallidus
,EF
Eptesicus fuscus
,LN
Lasionycteris noctivagans
,MC
Myotis
californicus
,MI
Myotis ciliolabrum
,ML
Myotis lucifigus
,
one asterisk P
0.05,
two asterisks
P
<
0.01,
three asterisks P
<
0.001 (Reproduced with permission from Snell-Rood
2012
)
<
for extra-pair fertilization. It is known that in many species song complexity
increases during the season, but the change in the repertoire is not easily distin-
guished from other factors. The grosbeak (
Guiraca caerulea
) sings a single song
type but rearranges the elements of its repertoire when the females are fertile, as
demonstrated by Ballentine et al. (
2003
), who found that male grosbeaks present a
more varied, more versatile arrangement of elements and have more syntax consis-
tency during the fertile period of the females than outside this period (Fig.
4.14
).
Conspecific competition usually is observed between males during the selection
and the maintenance of a territory. It seems strategic for competing males to enter
into a communicative contact to prevent trespassing in the neighbor territory. For
this reason, the acoustic communication is one of the best (and peaceful and
relatively inexpensive) methods to control a border, to respect the hierarchy, and
finally to have the necessary resources to raise a clutch. The rules by which two or
more males set the borders of each territory are quite complex. In the nightingale
(
Luscinia megarhynchos
) the singers can alternate their song, can overlap, or can be
neutral to the song of other males. Playback experiments carried out by Naguib
(
1999
) (Fig.
4.15
) have confirmed that during the overlap treatment males were
singing at a higher rate and interrupted the singing performance more frequently
than in alternating experiments. When males were exposed to alternating treatment,
however, they were singing at higher rates when they were exposed to overlap
treatment than when the alternating treatment was the first treatment they received.
This experiment confirms the importance of the time at which an individual
receives some conspecific stimuli.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search