Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 14.2 A diagram of the model human processor (adapted from Card et al.
1983
). d indicates a
half-life decay rate; l is a capacity; j is the modality of the storage; s is the time to do something
14.3.2.4 Explicit Information Processing Models: ACT-R
There is now a range of cognitive architectures that take as input a descriptive task
analysis that looks a lot like a computer program, and then simulate the cognitive
aspects of task performance, often with limitations simulated from vision and
motor performance. One of the most widely used architectures is ACT-R; others
include EPIC (Kieras et al.
1997
) and Soar (Laird
2012
; Ritter
2003
; Ritter and
Bibby
2008
).





























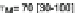
























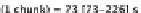

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search