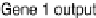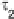Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
A Time-lagged Correlation Approach
1.3.2
In order to study the mechanism of the physiological response of the photosyn-
thetic cyanbacterium Synechocystis sp. to alternating light conditions, Schmitt Jr. and
his colleagues conducted time series experiments (Schmitt Jr. and Stephanopoulos,
). In these experiments, a culture of Synechocystis sp. was exposed to serial per-
turbations in light intensity;
samples were successfully hybridized to DNA mi-
croarrays. he time series experiments were set
min apart over periods of eight
and sixteen hours. he transcriptional networks of Synechocystis sp. that responded
to various light intensities were of interest. Postulating that the expression level of
target gene
follows the pattern of the input with a time lag, and similarly gene
follows its regulating gene
with another time lag, as depicted in Fig.
.
, Schmitt
Jr., Raab and Stephanopoulos (
) used a time-lagged correlation approach to in-
fer transcriptional interactions. Let x
i
denote the expression level of gene i at
time t and x
i
be the average expression level of gene i acrossthetimepoints.he
time-lagged correlation between genes i and j,proposedinArkinandRoss(
)
and Arkin et al. (
), is defined as r
ij
(
t
)
(
τ
)=
s
ij
(
τ
)
s
ii
(
τ
)
s
jj
(
τ
)
,wheres
ij
=
T
t
=
x
i
t
x
i
x
j
t
τ
x
j
and
τ
T.
(
(
)−
)(
(
+
)−
)
<
n matrix consisting of lagged-τ correlation between any
pair from n genes. he matrix
R
Let
R
τ
denote the n
(
)
can be used to rank the correlation and anticor-
relation between genes via a Euclidean distance metric d
ij
.hemetricD
ij
assumes
the form d
ij
(
τ
)
, where the maximal correlation
=(
c
ii
−
c
ij
+
c
jj
)
=
(
−
c
ij
)
c
ij
is a distance-based correlation that maps
genesthataretheleastcorrelated(forany τ)-the“farthest”apart.Byusingthematrix
D
, Schmitt Jr. et al. (
)were able to include both highly correlated and anticorre-
lated genes for further analysis. Using the modified time-lagged correlation method,
the input profile was employed as a “seed” to find genes that had time-lagged corre-
lated expression profiles, where the input signal profile consisted of the autoscaled
light intensity values at each time point.
=
max
τ
r
ij
(
τ
)
.hematrix
D
=(
d
ij
)
Figure
.
.
he time-lagged correlations between input and gene, and between cascades of genes