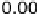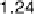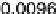Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure
.
.
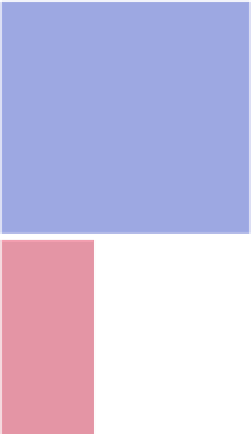
Mosaic plot for the arthritis data, using the maximum test and data-driven cut-off points
for the residuals
port the analysis of relationships with a single dependent variable. Residual-based
shadings can be used for model diagnostics, e.g., by using diverging color palettes to
code the sign and size of a residual. In addition, the non-significance of test statistics
can be visualized by using less colorful palettes. Using the maximum instead of the
χ
(or other) test statistic(s) allows for data-driven cut-offs in the diverging palettes
and precise diagnostic identification of the cells in conflict with the null hypothesis
of independence.
Selected Methods for Multiway Tables
12.4
In Sect.
.
we presented basic displays of two-way tables, based on the visualiza-
tion ofinformation in table cells that are arranged in rectangular form. Formultiway
tables, mosaicplots can be used directly by simply adding further splits for each ad-
ditional variable. For sieve and association plots, we apply the basic idea of mosaic-
plots to the table itself, i.e.,we simply nest the variables into rows and columns using
recursive conditional splits, given the margins. he result is a “flat” representation
of the multiway table that can be visualized in a way similar to a two-dimensional
table.
In the following, we will first treat specialized displays for exploratory purposes,
followed by model-based methods for conditional independence models.