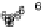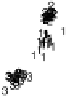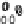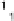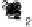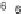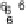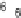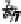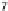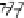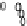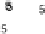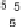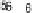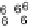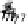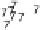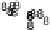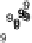Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure
.
.
Scatter plots of pen digits over KCCA-derived variates
(Fig.
.
) and the leading KCCA-derived variates (Fig.
.
)are given below. Differ-
ent groups are labeled with different digits. It is clear that the CCA-derived variates
are not informative regarding group labels, while the KCCA-derived variates are.
Kernel Cluster Analysis
10.5
Cluster analysis is categorized as an unsupervised learning method, which tries to
find the group structure in an unlabeled data set. A cluster is a collection of data
points which are “similar” to points in the same cluster, according to certain crite-
ria, and are “dissimilar” to points belonging to other clusters. he simplest clustering
method is probably the k-means algorithm (which can be used in a hybrid approach
with a kernel machine, or as a standalone method). Given a predetermined num-
ber of clusters k, the k-means algorithm will proceed to group data points into k
clusters by (
) placing k initial centroids in the space, (
) assigning each data point
to the cluster of its closest centroid, (
) updating the centroid positions and repeat
the steps (
) and (
) until some stopping criterion is reached (see MacQueen,
).
Despite its simplicity, the k-means algorithm does have some disadvantages. First,
apredeterminedk is necessary for the algorithm input, and different k's can lead
to dramatically different results. Secondly, suboptimal results can occur for certain