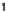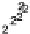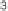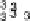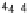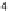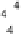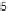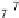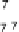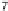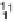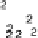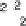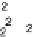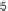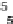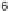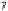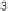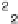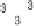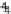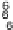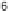Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Example
8
We usethe data set “pen-based recognition of hand-written digits” from
theUCIMachineLearning data archives foravisual demonstration ofnonlinear dis-
criminant usingKCCA.Weusethe
training instances forexplanatory purposes.
For each instance, there are
input measurements (i.e., x
j
is
-dimensional) and
a corresponding group label y
j
from
8
,
,
,...,
. A Gaussian kernel with a win-
(
dowwidth
is used to prepare the kernel data, where S
i
's are the
coordinate-wise sample covariances. A reduced kernel of size
equally stratified
over ten digit groups is used and serves as the K
in step (b) of the KCCA procedure.
We use y
j
, the group labels, as our K
(nokerneltransformation involved). Precisely,
S
,...,
S
)
Y
′
Y
′
n
Y
′
j
K
=
,
=(
,...,
,
,...
)
,
n
where Y
j
isa dummyvariable forgroup membership.If y
j
=
i, i
=
,
,...,
,thenY
j
hastheentry
atthe
thposition and
elsewhere.Nowwewant tosearchforre-
lationsbetweentheinputmeasurementsandtheirassociatedgrouplabelsusingCCA
and KCCA. he training data are used to find the leading CCA- and KCCA-derived
variates. Next,
test samples from each digit group are drawn randomly from the
test set
. Scatter plots of test data projected along the leading CCA-derived variates
(
i
+
)
Figure
.
.
Scatter plots of pen digits over CCA-derived variates
he testset has
instances in total, with around
instances on averagefor each digit.
For the sake of plot clarity and to avoid excess ink, we use only
test points per digit.