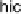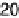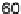Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Our goal is to identify the vehicle models for which the
hic
values are unusually
high, ater allowing for the effects of the predictorvariables. Since almost all the tests
involve two or more crash dummies, we will give two separate analyses, one for the
driver and another for the front passenger dummies. Ater removing tests with in-
complete values, we obtain
and
complete tests for driver and front passen-
ger, respectively. he tests for driver dummies involve
different vehicle models.
Figure
.
shows a histogram of the
hic
values for the driver data (the histogram
for front passenger is similar). here are
vehicle modelswith
hic
values greater
than
.heyarelistedin Table
.
,arranged bymodelyear, with thetotal number of
times tested and (in parentheses) the
hic
values that exceed
. For example, the
Nissan Maxima was tested eight times, of which five gave
hic
values greater
than
.
To identify the outliers ater removing the effects of the predictor variables, we
need to regress the response values on the predictors. he regression model must be
su
ciently flexible to accommodate the large number and mix of predictor variables
and to allow for nonlinearity and interactions among them. It must also be suitable
forgraphical display,astheoutlierswillbevisually identified. heserequirements are
well satisfied by a piecewise simple linear GUIDE model,which is shown in Fig.
.
.
he tree has three leaf nodes, partitioning the data according to
vehspd
. Beneath
each leaf node is printed the sample mean response for the node and the selected
signedlinearpredictor.Weseethat modelyearisthemostimportant linearpredictor
Figure
.
.
Histogram of
HIC
for driver dummy data. Shaded areas correspond to
HIC