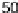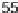Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
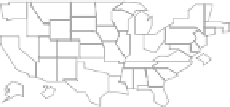
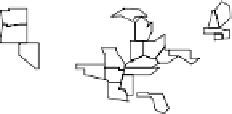
Figure
.
.
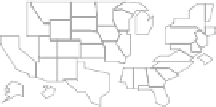
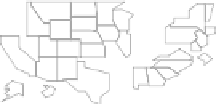
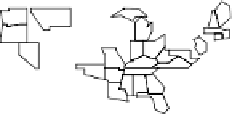
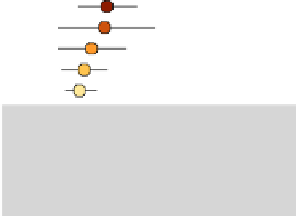
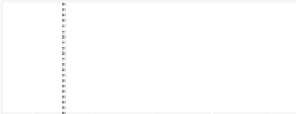
LM plots, based on data from http://www.statecancerprofiles.cancer.gov/micromaps,
showinglungandbronchuscancermortalityratesforwhitefemalesin
.helet column shows five
micromaps, with five states highlighted in different colors in each of the maps. he same color
information is used to link to the names of the US states in the middle column and to the data in the
right column. his data column displays US state mortality rates estimates (dots)and
%confidence
intervals (lines)
Many statistical graphics, such as dotplots, means with confidence bounds, box-
plots, and scatterplots, start with a strong foundation toward quality by encoding
information using position along a scale. Position along a scale encoding has a high
perceptual accuracy of extraction (Cleveland and McGill,
). Quality statistical
graphics oten represent estimate uncertainty and reference values using position
along scale encodings, provide grid lines to reduce distance effect problems in judg-
ing values against a scale, and follow the guidance of Tute (
) and others for
visually layering information. Good visual layering makes the most important in-
formation the most salient. Estimates are generally more important than confidence