Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
6WRFNVROXWLRQVDFLG
)UHVK
ZDWHU
1XWULHQW6ROXWLRQ
/HDFKDWH
(&
S+
1XWULWLRQ
&RQWURO
)UHVK:DWHU
0L[LQJ
WDQN
3XPS±)ORZ&RQWURO±
3UHVVXUH5HJXODWLRQ)LOWUDWLRQ
)UHVK
ZDWHU
/HDFKDWH
7DQN
6WRFNVROXWLRQVDFLG
'LVLQIHFWLRQ
1XWULWLRQ
&RQWURO
(&
S+
1XWULHQW6ROXWLRQ
'UDLQHG6ROXWLRQ
(&
S+
)UHVK:DWHU
0L[LQJ
/HDFKDWH
7DQN
3XPS±)ORZ&RQWURO±
3UHVVXUH5HJXODWLRQ)LOWUDWLRQ
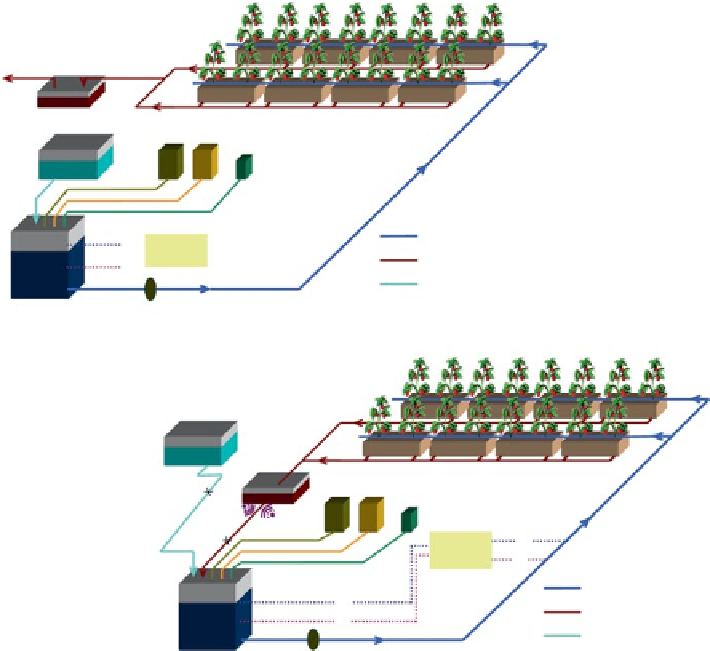
Fig. 10.17
Schematic diagram of a simple open- (
top
), and closed-loop (
bottom
) soilless culture
system. (Source: ecoponics, In: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Savvas
et al.
2013
. Reproduced with permission)
requires its own optimum growing technology and management approach with an
adapted fertigation system (Gruda
2009
).
Open and Closed-Loop Culture Systems
In soilless culture, methods of fertigation management and the recycling of nutrients
in solution are categorized as either an open or a closed-loop system (Fig.
10.17
). In
an open system, any excess water and nutrients is drained to waste and not recycled.
In a closed-loop system any drainage is captured, recovered and recycled. Closed
systems also increase the risk of spreading root diseases through the system; hence
treating the captured drainage water before recycling has to be considered (Wohan-
ka
1992
; van Os et al.
1999
). Most pure hydroponic systems are inherently closed