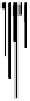Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 10.2
Midday PAR-
transmittance of the CCS,
measured at Zemach, Israel,
over 7 days from May 2005
to April 2006. Average data
from 6 PAR sensors (model
LI-190, Licor, Lincoln, NE,
USA).
Vertical bars
represent
two standard errors of the
mean. Daily rainfall mea-
sured at the nearby station is
indicated on the secondary
Y-axis. (Source: Möller et al.
2010
)
100
0
90
10
80
20
70
30
Precipitation
PAR transmittance
60
40
The Use of Additives to Plastic Covers
Different additives are used in order to improve the performance of plastic covers.
Ultra-Violet (UV)
Ultra-Violet stabilizers, which are incorporated into the poly-
mer matrix of greenhouse covers, stabilize the harmful UV radiation from entering
into the greenhouse and allow for maximum light transmission. When used along
with anti-oxidants they protect the film from photo as well as thermal degradation
and help in proper and maximum light transmission, by increasing the durability
of plastic materials (NN
2012a
). UV additives block the invasion of insects into
the greenhouse and protect the crop from infestation by insects and the spread of
viruses (Antignus et al.
1998
).
Infra-red (IR)
During nighttime, outside temperatures are lower than inside, so the
heat that accumulates inside the greenhouse during the day is lost to the outside by
irradiation (NN
2012a
). During the night the temperature outside the greenhouse
falls below the temperature within the greenhouse. As a result there is loss of heat
from the greenhouse by radiation towards the outside and the greenhouse tempera-
ture drops. This transfer mechanism takes place by the infra-red radiation. To pre-
vent this radiation loss, mineral based additive or special polymers are incorporated
within greenhouse films that help to maintain the temperature within the green-
house and insulate the plants from the cold injury and temperature variation, save
energy for nighttime heating and prevent the accumulation of heat during the day in
warm climates (Hemming et al.
2006
).
Anti-Fog/Anti-Drip Effect/Anti-Condensation
Condensation of water vapor, results
in formation of droplets on the inside surface of the greenhouse film. This has a neg-
ative effect on the crop because there is a reduction in morning light transmission,
when most condensation may take place (Fähnrich et al.
1989
), droplets falling on
the foliage which can make plants more prone to diseases; and the burning of petals