Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
increased temperature profiles of 25-30 °C during fermentation may be encour-
aged as this expedites the fermentation process and enhances extraction of phenolic
compounds, including pigmented anthocyanins from the berry skin mass thereby
producing wines with more intense colour. A most important consideration regard-
ing temperature profiles of red ferments is to ensure that the maximum tempera-
ture achieved during fermentation does not exceed the threshold for cell membrane
damage as this will lead to the potential loss of cytoplasmic constituents, which
along with ethanol toxicity may lead to sluggish or stuck fermentations. Most red
ferments are managed to ensure temperature do not exceed 30 °C (Fugelsang and
Edwards
2007
).
Ethanol Production
The outcome of carbohydrate metabolism by yeasts during fermentation is princi-
pally ethanol. The conversation of fermentable carbohydrate proceeds by the glyco-
lytic pathway common to all eukaryotic cells such that two molecules of pyruvate
are formed from each molecule of glucose or fructose. During fermentation condi-
tions rapidly become anaerobic and the production of ethanol by yeast is the funda-
mental driver for the continued production of energy from the glycolytic pathway.
It is the production of ethanol concomitant with the regeneration of the electron
transporting molecules NAD + from NADH that enables further energy to be pro-
duced to drive the cellular demands for biomass production. The net reaction of the
glycolytic pathway is summarised below:
Glucose + 2ADP + 2Pi + 2NAD
+
→ 2Pyruvate + 2ATP + 2NADH + 2H
+
+ 2H
2
O
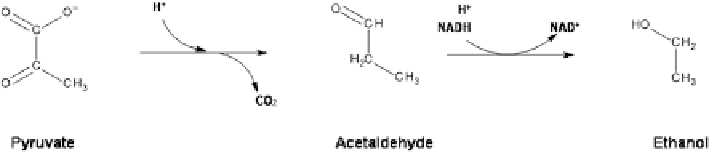
Conversion of pyruvate to ethanol proceeds via acetaldehyde with loss of a carbon
moiety thereby producing carbon dioxide. This is shown in the following reaction:
Thus Overall the conversion of glucose (or fructose) by yeasts to ethanol during
alcoholic fermentation can be summarised as:
CH O
→
2CHOH
+
2CO
+
2ATP
626
25
2
Glucose
Ethanol
Carbon dioxide denos
inetriphosphate