Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
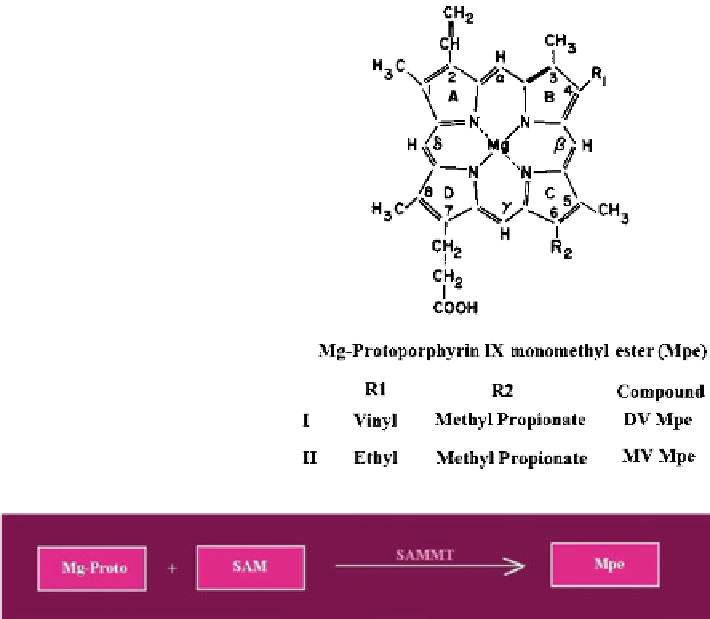
Fig. 7.8 The Mg-Proto
monomethyl ester
(Mpe) pool
Fig. 7.9 Conversion of Mg-Proto to Mpe by SAMMT
7.2 The Mg-Proto Monomethyl Ester (Mpe) Pool
Protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (Mpe) pool is the precursor of the Pchlide
a
pool. The role of Mpe as an intermediate in the Chl biosynthetic pathway was
based on the detection of Mpe in X-ray
Chlorella
mutants inhibited in their capacity
to form Chl (Granick
1961
). It was conjectured that since the mutants had lost the
ability to form Chl but accumulated Mpe, the latter was a logical precursor of Chl.
On the basis of absorbance spectroscopic analysis, Mpe was assigned by Granick a
DV chemical structure. Mpe was also detected in barley leaves incubated with ALA
and 2,2
0
-dipyridyl (Dpy) (Granick
1961
). In this case too, the accumulated Mpe was
assigned a divinyl (DV) chemical structure (Fig.
7.8
).
Mg-Proto is converted to Mpe by transfer of a methyl group from (
)
S-adenosyl-L- methionine (SAM) to Mg-Proto. The reaction results in the methyl
esterification of the propionic acid residue at position 6 (ring C) of the macrocycle.
The reaction is catalyzed by (
) S-adenosyl-L-methionine-magnesium protopor-
phyrin methyl transferase (SAMMT) (Fig.
7.9
).
The occurrence of SAMMT was first reported in
Rhodopseudomonas spheroides
(Gibson et al.
1963
). The enzyme was confined to the chromatophores to which it was
Search WWH ::

Custom Search