Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
7.3. READ-ONLY MEMORY
Random access as well as cache memories are examples of volatile memories. A
volatile storage is defined as one that loses its contents when power is turned off.
Nonvolatile memory storages are those that retain the stored information if power
is turned off. As there is a need for volatile storage there is also a need for nonvo-
latile storage. Computer system boot subroutines, microcode control, and video
game cartridges are a few examples of computer software that require the use of
nonvolatile storage. Read-only memory (ROM) can also be used to realize combi-
national logic functions.
The technology used for implementing ROM chips has evolved over the years. Early
implementations of ROMs were called mask-programmed ROMs. In this case, a made-
to-order one time ROM is programmed according to a specific encoding pattern sup-
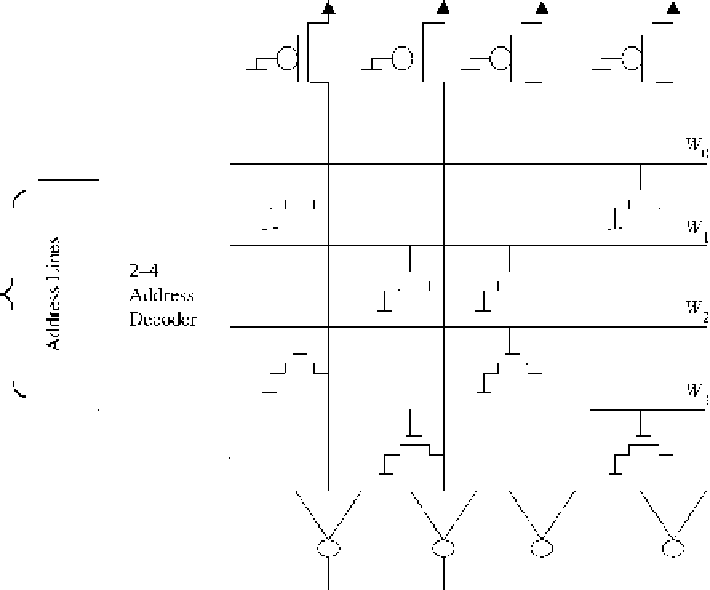
plied by the user. The structure of a 4
4 CMOS ROM chip is shown in Figure 7.20.
In this figure an n-type transistor is placed where a 1 is to be stored. A two-to-four
address decoder is used to create four word lines; each is used to activate a row of
transistors. When a 1 appears on the word line, the corresponding transistors will be
turned on, thus pulling the corresponding bit line to 0. An inverter at the output of the
Figure 7.20 Example of a 4
4 CMOS ROM chip
Search WWH ::

Custom Search